Painful Skin Boils? It Could Be Furuncles or Carbuncles
Furuncles and carbuncles are bumps filled with pus that form on the skin. They are skin abscesses that can be mistaken for a painful pimple at first because they begin as a small bump.
However, carbuncles and furuncles are areas of staph infection; hence, it is important to recognize them and seek treatment if the infection does not resolve. About 3 in 100 people visiting their physician for a skin condition are diagnosed with a furuncle. Carbuncles, on the other hand, are less common.
This article discusses furuncles and carbuncles in detail, including their characteristics, causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, and treatment options. Tips on how to prevent a furuncle or carbuncle are also covered.
What Are Furuncles and Carbuncles?
What Is a Furuncle?
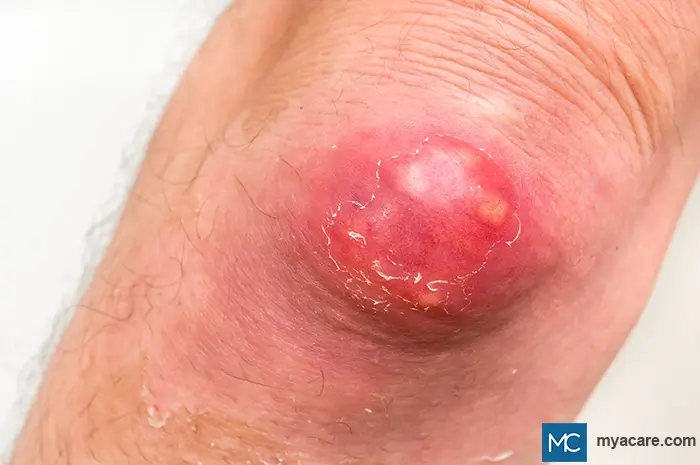
A furuncle, commonly called a boil, is a raised area of skin that develops due to bacterial infection. It forms under the skin in the armpits, face, buttocks, and thighs. A furuncle initially presents as a painful red or purple-colored bump that eventually grows and fills with pus. In due course, the boil breaks apart and drains.
What Is a Carbuncle?
This term refers to a group of boils, i.e., a cluster of furuncles. A carbuncle usually develops on the neck or the back. However, you can sometimes get a carbuncle on the face, buttocks, or any other part of the body. A carbuncle involves several infected hair follicles and, hence, boils that are connected beneath the skin.
Causes and Risk Factors
Staphylococcus aureus is the bacterial species most often responsible for boils or carbuncles. S. aureus is a bacterium commonly found on the skin that can sometimes cause infection. You can also develop MRSA-related boils. MRSA infections are more common in people who have been in hospital.
Risk factors
- Nasal carriage of S. aureus - The presence of the bacteria in your nose increases the likelihood of developing a furuncle.
- Compromised skin barrier and pre-existing skin conditions - Skin conditions like eczema can make it more likely to develop a furuncle.
- Weakened immune system - A strong immune system helps fight infection. If you have cancer or diabetes, you may be more likely to develop boils due to a compromised immune system.
- Close contact with an infected person - You can become infected if you have close contact with a person who has a boil or carbuncle. Sharing towels and personal items can also spread the infection.
- Poor hygiene - Irregular bathing can lead to the accumulation of sweat and dead skin, which could result in the formation of boils.
Signs and Symptoms
Furuncle Symptoms
A furuncle begins as a small red bump on the skin that feels sore. Over time, the bump increases in size and fills with pus. When it fills with pus, a central white or yellow area is present in the bump. It progressively becomes more painful, and pus may start to ooze from the boil.
Carbuncle Symptoms
A carbuncle also begins as a small red painful bump that grows and fills with pus. However, comparing a carbuncle vs. a furuncle, the former is a more severe infection, as many hair follicles are infected, resulting in a larger bump. Further symptoms of carbuncles include the presence of several areas of pus that drain. Fever, chills, and fatigue are systemic symptoms that may be present if you have a carbuncle.
Complications
Complications of boils and carbuncles are rare but can include the spread of the infection, leading to sepsis, meningitis, or cellulitis. Carbuncles may become life-threatening if you develop a complication like sepsis. The bacteria from a skin carbuncle can also spread through the bloodstream to internal organs, resulting in, for example, a renal carbuncle (i.e., renal cortical abscess).
Scarring is also more common if you have a carbuncle. A chronic recurrence of furuncles is when three or more boils develop in a year. This may indicate the presence of resistant bacteria, staph in the nose, or an underlying condition, such as diabetes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on a clinical examination. A physician will examine and note the area of skin that is affected. In severe or recurrent cases, a pus culture and blood tests may be done.
Your medical history may determine if you are at risk for boils or carbuncles. It may also help your physician personalize treatment.
Differentiating furuncles and carbuncles from other skin conditions is important in determining the treatment needed.
Furuncle vs. Folliculitis
A furuncle is a swollen lump that is full of white pus and is painful. Folliculitis is an inflammation of a hair follicle and is a red and itchy area, potentially containing pus in the follicle.
Acne cysts and Boils
A cyst occurs as a painless bump under the skin, while a boil is a painful, red bump on the skin .
Carbuncle vs Sebaceous Cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a dome-shaped bump under the skin that happens when sebaceous glands become blocked, whereas a carbuncle is a group of painful boils found deep in the skin and is due to bacterial infection.
Carbuncle and Abscess
An abscess is an area of infection that contains pus. Skin carbuncles and boils are types of abscesses. You can get an abscess in other areas of the body, for example, a tooth.
Treatment
Furuncle and carbuncle treatment follow the same course, but depend on the severity of the condition. Sometimes medical treatment is not needed, and home care is sufficient.
Home Care
A small boil can be treated at home, but you should consult your physician if you have any concerns.
- Warm compresses. Apply a warm compress or washcloth to the boil several times a day for about 10 minutes. This helps promote drainage of the boil and may also help as a carbuncle home remedy.
- Hygiene and antiseptic cleansing. Clean the boil or carbuncle using antibacterial soap. You can also do this once the boil drains. Cover the area with a sterile bandage.
- Avoid squeezing or picking boils or carbuncles. This can worsen your condition by spreading the infection.
Medical Treatment
Seeing a doctor is often needed to get rid of carbuncles, since they are deeper infections than furuncles, but even a furuncle may need medical treatment if it does not improve.
- Incision and drainage by a healthcare professional may be necessary if a furuncle does not resolve on its own. Carbuncles often need drainage by a doctor as they are larger and deeper infected areas. If you have a carbuncle, you may also have a fever and systemic response.
- Carbuncle treatment often includes oral or topical antibiotics. These are also recommended if drainage is insufficient in helping a furuncle heal or if the nodule is more than 5 mm in size. Antibiotics are usually recommended to treat the abscesses of carbuncles. NSAIDs may help with pain relief.
When to See a Doctor
- Lesion does not drain or improve. This indicates that the infection is not clearing up.
- Increasing size, pain, or redness. This typically shows that the infection is spreading.
- Systemic infection. More common with carbuncles, this can lead to fever, swollen lymph nodes, and tiredness.
- Recurrent/multiple boils. Recurring boils may be a sign that you have a methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infection.
- Boils on the face or spine. The risk of complications may be greater if you have boils on your face or spine. For instance, infection from facial boils could spread to the brain, and boils on the spine could cause neurological damage.
Prevention Tips
Personal hygiene is vital in helping prevent boils. Bathe regularly and avoid wearing clothes that chafe and irritate the skin. Using a moisturizer may not be enough to stop boils, but it may help indirectly by protecting the skin. Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels, clothing, razors, and deodorant, since this can spread bacteria. Handwashing is also important in preventing the spread of bacteria.
Ensure proper wound care and treat any injuries promptly. Manage any underlying conditions, such as diabetes, which can make you susceptible to boils.
Outlook and Recovery
Most furuncles and carbuncles resolve without complications if treated early. Recurrent cases may require further evaluation to ascertain the cause and the most effective treatment to prevent recurrence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a carbuncle be cancerous?
No, a carbuncle is not cancerous, but it is more common in people who have cancer and other conditions in which the immune system is compromised.
Can a carbuncle heal on its own?
Yes, however, it is advisable to consult a doctor if it persists for more than two weeks, is on your face or spine, or if you have a fever.
How long does a furuncle take to heal?
A furuncle usually heals after a few weeks.
Can diet affect boil formation?
Yes, since the nutrients you take in with food can impact the health of your immune system.
What is your body lacking when you get boils?
Being deficient in vitamin A may increase the likelihood of developing boils, since this nutrient is important for healthy skin.
To search for the best Dermatology Healthcare Providers in Croatia, Germany, Greece, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Slovakia, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, the UAE, UK, the USA, please use the Mya Care search engine.

Dr. Rae Osborn has a Ph.D. in Biology from the University of Texas at Arlington. She was a tenured Associate Professor of Biology at Northwestern State University, where she taught many courses to Pre-nursing and Pre-medical students. She has written extensively on medical conditions and healthy lifestyle topics, including nutrition. She is from South Africa but lived and taught in the United States for 18 years.
References:
Featured Blogs



