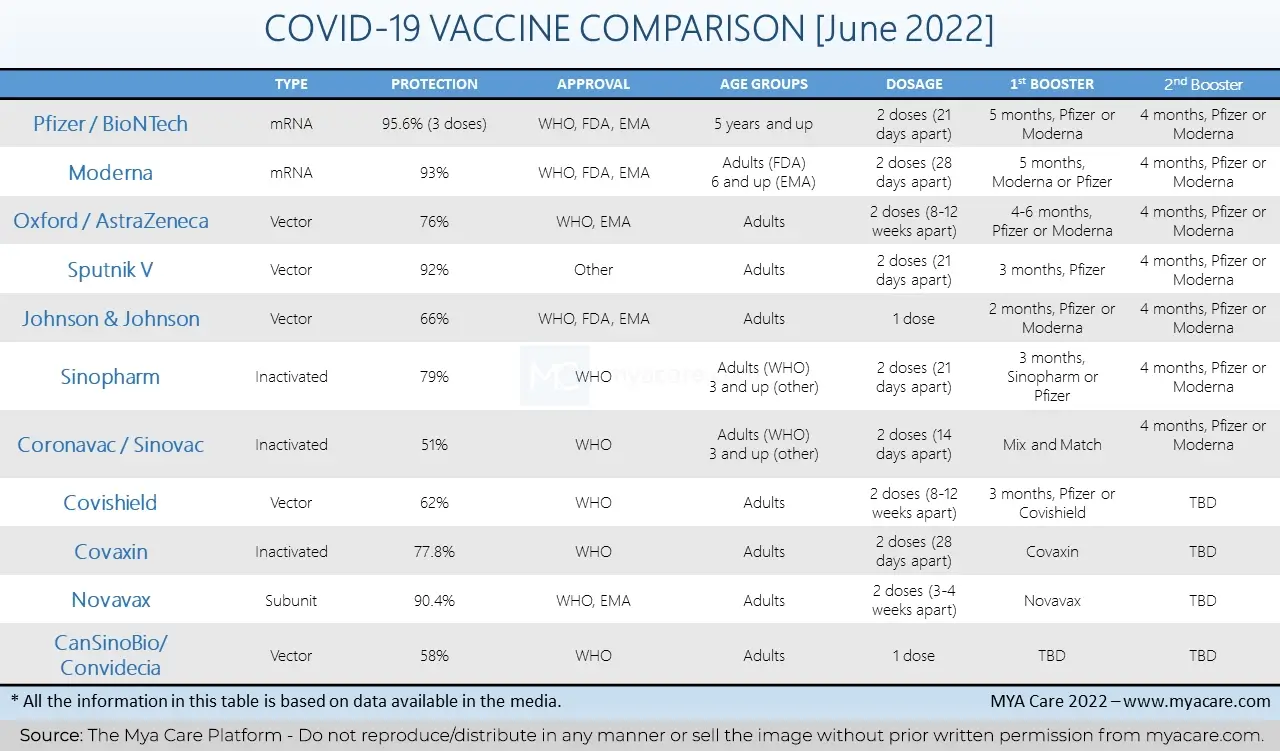
Comparison of COVID-19 Vaccines
Mixing And Matching Covid-19 Vaccines
Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness With Time
Studies Comparing Different Vaccines
Vaccines Against New Delta Variants
Vaccines Against New Omicron Variant
This article was originally published in November 2020 and was updated to include 2021 and 2022. Please note however, the article has not been updated since the end of 2022 and therefore it might not include current updates.
In the year 2021, humanity witnessed the biggest global vaccination campaign in history. More than 9 billion doses of the corona vaccine have been administered around the globe so far.
We now have several vaccines to combat the corona pandemic. But how do these vaccines compare? How are they different? Which one is the best COVID-19 vaccine?
Pfizer/BioNtech and Moderna were the most groundbreaking of all vaccines. They introduced the fairly new (and thankfully, successful) mRNA vaccine technology. Sputnik V, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, Covishield, Sinopharm, Novavax, and others followed soon after.
This article will compare the different COVID vaccines in light of what we’ve learned in 2021, with monthly updates of what we learn in 2022.
PFIZER/BIONTECH VACCINE
The Pfizer vaccine was the first-ever approved corona vaccine. It was also the first mRNA vaccine in history to be authorized for public use. It was produced by a collaboration between the American pharmaceutical giant, Pfizer, and an innovative German biotechnology firm, BioNTech.
Soon after the approval, the vaccine gained wide support from the WHO and health authorities all around the world. It’s now regarded by many as the best COVID vaccine available, however, this remains subjective to many factors.
Technology and Dosage
The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine introduced a new technology to the vaccine market; mRNA vaccines. These vaccines are based on genetic mRNA molecules. The mRNA (messenger RNA) carries the genetic code for the “spike” protein, an antigen specific for the SARS-CoV-2.
Once injected, the mRNA enters your body cells, making them produce the spike protein themselves.
This allows your immune system to prepare to combat the actual infection if it happens.
The vaccine is given in 2 doses, with 3-4 weeks between the first and second dose. A third booster dose with the same vaccine is now recommended after 5-6 months.
Moreover, Pfizer is recommended as a booster for those who received vaccines from other classes. This includes AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Sinopharm (non-mRNA vaccines).
Pfizer has announced that a new booster 4th dose is being designed, and should be ready in March 2022. The fourth Pfizer shot is designed to specifically protect against the Omicron variant. Pfizer is aiming to completely prevent infection, rather than just preventing hospitalization.
Approval
The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine is fully approved by the FDA, WHO, EMA, and almost all international health authorities.
Effectiveness (with Time)
Ever since the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine got approved in December 2020, there have been many studies to assess its effectiveness.
The original trial by Pfizer showed that the 2 shots of the vaccine were 95% protective against COVID-19.
However, scientists observed that immunity wanes with time, and that a 3rd dose re-boosts protection against the coronavirus. This is why now, the term “fully vaccinated” means 3 jabs and not just two.
Three doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine were found to be protective against disease in 95.6% of individuals. The study analyzed data from nearly 10,000 individuals who got their third booster dose.
Concerns
There have been many concerns and misconceptions regarding mRNA vaccines. However, the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine proved to be safe and effective in combating the pandemic.
Claims that mRNA vaccines alter your DNA, affect pregnancy, or cause long-term illnesses remain without any supporting evidence.
Side effects of Pfizer/BioNTech are mostly mild. There’s no data to suggest any safety concerns.
Age Groups
The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine has been approved for both children (ages 5-17) and adults:
- The FDA and EMA have approved the vaccine in children aged 5 and over
- The WHO has recently approved a booster dose of Pfizer/BioNTech in children aged 12 and up. So far, this is the only WHO-approved booster vaccine in children.
- The FDA also more recently approved a second booster dose for immunocompromised children aged 12 and older.
- A fourth Pfizer dose is now recommended in those aged 50 and older
February 11, 2022 Update
- A 4th dose of Pfizer is now being recommended in Abu Dhabi as a booster shot
- A new study showed that a Pfizer 3rd booster shot was 90% effective against Omicron
- Pfizer has announced plans to apply for FDA authorization for children aged 6 months to 4 years
March 4, 2022 Update
- A new study found that a fourth dose of Pfizer does increase antibodies against Corona. However, it only provides a slight boost in immunity against the virus. The authors of the study suggested that a 4th Pfizer shot might be beneficial only in at-risk groups (e.g. immunocompromised or healthcare workers)
- The FDA is reviewing data to determine whether a second Pfizer booster (4th shot) is necessary or not.
- A new study showed that the Pfizer vaccine is less effective in children aged 5 to 11 years old. Authors found that the vaccine protected against severe disease, but had minimal ability to prevent infection.
- A study from Hong Kong showed that teenagers were 7 times more likely to develop myocarditis after Pfizer vaccination. The statistical analysis showed that in this age group, the rate of myocarditis was 39 cases in every 100,000 vaccinated teens compared to 5 in every 100,000 vaccinated adults.
- As for the Pfizer vaccine’s effectiveness with time, a new study from Sweden showed that the protection wanes after 4 to 6 months. The initial protection from Pfizer is 92% after the second dose, and this decreases to 47% in 4-6 months.
- A new study showed that the effectiveness of two doses of Pfizer against Omicron was a only 8% after 6 months. However, a third booster dose restores good levels of protection against the dominant variant.
April 5, 2022 Update
- A recent study, under peer review, was done on 500,000 patients from january to february 2022. The study found that people aged between 60-100 years who received a second booster shot (fourth dose) instead of just one had a 78% decrease in death rate.
- According to a study published by the CDC, the risk of myocarditis was higher in patients infected with the corona virus than those who received the Pfizer mRNA vaccine. The findings showed that a SARS-CoV2 infection posed a myocarditis risk that is 1.8-5.6 times higher when compared to its risk after the second shot of the vaccine. These findings are in support of the recommended mRNA vaccines for eligible patients aged 5 years and above.
- A recent WHO newsletters investigated a potential link between the Pfizer vaccine and hearing problems. The investigation showed that 80% of 367 reported tinnitus cases following covid vaccination were developed after the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
- The FDA has recommended a fourth Pfizer dose in those aged 50 and older and those who are immunocompromised, given 4 months after the 3rd dose.
May 6, 2022 Update
- According to new data analysis, a high immune response was recorded in children of ages between 5 and 11 years following a booster (third) dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
- The FDA has set aside the dates of June 8, 21, and 22 for Pfizer to discuss data on their Covid-19 vaccine in the younger population (children younger than 5).
- A recent study published in the New England Journal of Medicine investigated the effects of a fourth dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine on people aged 60 years or older. The study showed that in the fourth week after a fourth dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the rate of severe Covid-19 infection was lower than in people who only got 3 doses.
- New research investigated the durability and effectiveness of Pfizer’s Covid-19 booster (third) shot in patients aged 18 years or older. Researchers found that the three doses of the vaccine were initially effective in protecting against hospitalization and emergency room visits due to both the delta and omicron variants. However, this efficacy starts to wane off 3 months after receiving the third shot.
June 6, 2022 Update
- According to CNN health, Pfizer and BioNTech have completed submitting their request to the FDA to authorize the emergency use of their Covid-19 vaccine in children of ages between 6 months to 5 years.
- A third dose of the Pfizer and BioNTech Covid-19 vaccine in children between the ages 6 months and 5 years was found to be safe and effective in producing an immune response against the virus, according to data from a phase2/3 trial.
- Pfizer and BioNTech were granted by the FDA emergency use authorization for the booster dose of their Covid-19 vaccine in children between the ages of 5 and 11 years old.
- Pfizer and BioNTech have updated their Covid-19 vaccine supply agreement with the European Commission.
August 5, 2022 Update
- The FDA amended the emergency use of the Pfizer-BioNTech Covid-19 vaccine to include children aged 6 months through 4 years old. The vaccine was already approved for kids 5 years and older.
- Pfizer and BioNTech gained FDA approval for their COMIRNATY® Covid-19 vaccine for children aged 12 through 15 years old.
- On July 2022, Pfizer and BioNTech announced the beginning of a phase 2 study to evaluate an enhanced version of their mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. The Next Generation Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vaccine candidate is a bivalent vaccine with an enhanced spike protein design.
- A new study revealed that a booster shot of the Pfizedr/BioNTech Covid-19 vaccine can increase protection against the newly emerged BA.4/5 Omicron variants.
- In a more recent study, the authors concluded that a fourth dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vaccine reduces breakthrough infection rates. This can help increase the protection of hospital staff against the Covid-19 virus and mitigate the shortage in medical staff due to coronavirus infections.
September 8, 2022 Update
- A recent study done in Ontario, Canada, investigated the effectiveness of the BNT162b2 Pfizer novel coronavirus vaccine against symptomatic Omicron infections in children aged 5-11 years old. The study showed that two doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine were effective in protecting individuals between 5-11 years old against symptomatic Omicron infections and severe outcomes. However, that protection waned around 60 days after the second dose.
- Pfizer/BioNTech announced results from a Phase 2/3 trial evaluating the efficiency of 3 doses of their COVID-19 Vaccine in children 6 months through 4 years of age. The results of the trial confirmed that the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine was well tolerated in these age groups and also provided young children with a high level of protection against the Omicron BA.2 strain.
- In a large retrospective study, authors reported findings regarding the safety of mRNA novel coronavirus vaccines in pregnant women. The most common side effects of the Pfizer/BioNTech Covid vaccine during pregnancy were malaise (a general feeling of illness) and myalgia (muscle aches and pains) following two doses of the vaccine. Other side effects included headaches and migraines. The study reported that serious health events in pregnant women following 2 doses of the Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine were rare.
- A study published in JAMA Network Open investigated the effectiveness of the Pfizer and BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in individuals aged 12-18 years in South Korea. According to the research, 2 doses of the BNT162B2 vaccine were effective in protecting that age group against critical COVID-19 infections. However, that protection decreased 30-60 days after the administration of the second dose.
- Another study investigated the effectiveness of the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine against long-term COVID-19 symptoms. Researchers concluded that two doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech Covid-19 mRNA vaccine could protect against post-COVID-19 syndrome, also known as long coronavirus disease 2019 or Long COVID.
- On August 26, 2022, Pfizer/BioNTech completed their submission to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for a booster dose of their Omicron BA.4/BA.5-adapted bivalent COVID-19 vaccine for individuals 12 years of age and older. This came after pre-clinical data revealed that a booster dose of the Pfizer/BioNTech Omicron BA.4/BA.5-adapted bivalent COVID-19 vaccine was efficient against Omicron variants BA.1, BA.2, and BA.4/BA.5, in addition to the original strain.
- In an announcement on August 31, 2022, the Food and Drug Administration authorized the emergency use of the bivalent Covid-19 vaccine booster shots from Pfizer in individuals 12 years of age and older. The bivalent Pfizer mRNA vaccine combines two mRNA components; one from the original COVID strain, and another that targets the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron sublineages. People can receive the Pfizer bivalent vaccine, also called “updated booster”, as a single booster shot at least 2 months after primary or booster vaccination.
- Similarly, The CDC has approved using an updated COVID-19 booster from Pfizer for individuals aged 12 years and older.
- In September 2022, Pfizer and BioNTech’s Omicron BA.1-Adapted Bivalent COVID-19 Vaccine for individuals 12 years and older received positive feedback from the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). The European Commission is expected to review the recommendation of the CHMP and make a final decision soon regarding the Omicron BA.1-Adapted vaccine by Pfizer.
December 27, 2022 Update
- In November 2022, Pfizer and BioNTech received positive feedback on their Omicron BA.4/BA.5-adapted bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster for children 5 through 11 years of age in the European Union.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) recommended the marketing authorization of the booster dose for children between the ages of 5 and 11. The European Commission will review this recommendation and should make a decision soon.
- A study published on December 1st, 2022, investigated the possible side effects of different COVID-19 vaccines in more than 17 million elderly persons aged 65 years and older.
The study detected four outcomes that met the threshold for a statistical signal following vaccination with the BioNTech, Pfizer Covid vaccine (BNT162b2), including pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lungs) and acute myocardial infarction (heart attack).
However, the study included elderly patients aged 65 years and older, and the analysis did not consider the patient’s risk factors. The authors warn that these results do not prove that vaccines cause the mentioned safety outcomes. The FDA still recommends the Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine for children and adults.
Contrary to viral claims on social media, the study did not find that the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine caused blood clots.
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared the updated (bivalent) Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for use in children as young as 6 months of age.
- The CDC also expanded the age groups that can receive the Pfizer bivalent Covid vaccine as their third primary dose. Children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years can now receive a Pfizer bivalent booster shot after completing their primary vaccination series.
MODERNA VACCINE
Moderna was the second approved mRNA vaccine against COVID. After almost a year of being approved, we now know that it’s safe and effective in preventing corona.
Technology and Dosage
The Moderna vaccine uses the same basic technology as Pfizer/BioNTech - it’s an mRNA vaccine.
The Moderna jab is given in 2 doses, 28 days apart. The third booster dose of Moderna is given with the same vaccine after 5-6 months of the second one. More recently, the fourth booster dose became recommended for patients 50 years or older and 12 years or older immunocompromised patients at least 4 months after receiving their third shot.
Moreover, the Moderna vaccine is also recommended as a booster for those who received vaccines from other classes. This includes AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Sinopharm (non-mRNA vaccines).
Moderna has also announced that they’ll be working on a booster dose to specifically combat newer corona variants, like Omicron.
Approval
Moderna is approved by the FDA, WHO, EMA, and almost all international health authorities. It has received worldwide acceptance and is generally considered one of the top COVID-19 vaccines available in the market.
Effectiveness (with Time)
Two doses of Moderna were found to be 93% effective in preventing hospitalization in patients at 4 months after the second dose. However, researchers have found that protection provided decreased to 58% after 6 months.
A third dose, however, will boost immunity levels, according to the company, giving more protection against new variants like Omicron.
Age groups
In the USA, Moderna is approved only for those aged 17 and up. In Europe, however, the vaccine is approved for children aged 6 and up.
The EMA’s approval came after a large study by Moderna showed that their vaccine is safe and effective in children aged 6 and up.
February 11, 2022 Update
- The FDA has given Moderna full approval, becoming the second vaccine to be fully FDA approved for COVID-19. As opposed to emergency use authorization, full approval removes more restrictions on a vaccine’s distribution and marketing.
- A new study showed that a Moderna 3rd booster shot was 90% effective against Omicron
- Moderna has reached phase II of testing for their vaccine booster against Omicron. The company also announced plans to create a shot that targets all variants to be the equivalent of the yearly flu shot.
March 4, 2022 Update
- According to a new study, protection after 2 doses of Moderna decreases only slightly with time, decreasing from 97% to 71% after 6 months.
- A new study showed that the effectiveness of two doses of Moderna against Omicron was only 15% after 6 months. Nevertheless, the authors found that a third booster dose restores immunity effectively.
- Moderna’s specific Omicron booster was not found to provide increased protection against Omicron when compared to a booster with the original Moderna vaccine. These results were concluded by a small study, however, more research is needed to confirm.
April 5, 2022 Update
- According to a recent study, the Moderna vaccine provokes the body to produce antibodies different from the antibodies produced after the Pfizer vaccine. This difference in the type of produced antibodies could explain the difference in the two vaccines’ efficacy.
- The NIH released that a Moderna investigational vaccine has entered Phase 1 of a clinical testing. The new vaccine, named mRNA-1273.351, is designed to protect against the B.1.351 SARS-CoV-2 variant which was first identified in the Republic of South Africa.
- After positive clinical trial data, Moderna will be seeking authorization for its COVID-19 vaccine for children between 6 months and 6 years old in the coming weeks.
- During the NCCN 2022 Annual Conference, a presented study suggested that the Moderna vaccine was more effective in CLL cancer patients than other vaccines, including the Pfizer-BioNTech covid vaccine. Treated CLL patients who received the Moderna vaccine had a 51% antibody response rate, higher than the response rate with the Pfizer vaccine (29%).
- The FDA has recommended a fourth Moderna dose in those aged 50 and older and those who are immunocompromised, given 4 months after the 3rd dose.
May 6, 2022 Update
- Moderna announced last month a recall of one lot of its Covid-19 vaccine from Norway, Poland, Portugal, Spain, and Sweden. The lot, which was manufactured in Spain, was withdrawn because a foreign body was found in one of its vials at a vaccination center in Malaga, Spain. However, to date, no safety or efficacy concerns were reported in individuals who were vaccinated from this lot. None of the Moderna Covid-19 vaccines were recalled from the USA.
- A recent study published in nature communications compared the effectiveness of a second dose of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. The data revealed that immunization with a second shot of Moderna vaccine provided slightly more protection against Covid-19 infection than Pfizer’s second dose. However, both vaccines were equally effective in protection against hospitalization, ICU admission, and death/hospice transfer after a second dose.
- Moderna aims to gain FDA approval for its Covid-19 vaccine for young children (6 months to 6 years of age). The FDA expects to receive relevant data and information from Moderna in early June.
- Moderna is also currently conducting studies on booster doses for children of different age groups.
- In a recent press release, Moderna shared clinical data on their first bivalent booster vaccine candidate (mRNA-1273.211). This bivalent booster vaccine includes 9 spike protein mutations based on the Beta variant. The data showed that a booster shot of the new bivalent vaccine candidate was able to induce a higher antibody response than Moderna’s currently approved mRNA-1273 booster shot.
June 6, 2022 Update
- A new study on the efficacy of the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine was published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study revealed that two doses of the vaccine were able to generate safe and robust immune responses in children between the ages of 6 and 11 years.
- A committee of FDA independent experts is expected to meet on June 15 to review the safety and efficacy of the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine on infants and toddlers.
- Second generation booster of the Moderna vaccine is expected to be launched in the late summer of 2022 according to Moderna CEO Stephane Bancel. The second generation Covid-19 booster vaccine will be adapted to two variants of the virus including the Omicron variant.
- The Moderna Covid-19 vaccine is suffering from a demand problem according to a statement by Stephane Bancel at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. Bancel stated that they’re in the process of destroying 30 million doses of expired Moderna vaccines.
August 5, 2022 Update
- The FDA authorized the emergency use of the Moderna vaccine in children 6 months or older after it was determined safe and effective in these age groups.
- Moderna announced in a recent statement the preliminary data analysis of its new Omicron-containing booster vaccine. The early results show that Moderna’s new bivalent booster shot was effective in protecting against the Omicron coronavirus variant.
- A recent study investigated the effectiveness of a fourth dose of Covid-19 mRNA vaccines (Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech). The authors concluded that a fourth dose of the coronavirus vaccine was necessary to improve protection against Covid-19; 3 doses are not enough.
- A new study published in Nature evaluated how well vaccinated individuals were protected against the new BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants. The authors concluded that the newly emerged Omicron subvariants BA.4/5 were more resistant to mRNA coronavirus vaccines such as Moderna and Pfizer vaccines.
- The CDC published a new study that concluded that a third Moderna or Pfizer vaccine booster dose can increase the protection against Omicron BA.1 and BA.2/BA.2.12.1 sublineages. Moreover, a fourth dose was able to provide additional protection to adults aged 50 years and older.
- Health Canada has authorized the use of Moderna coronavirus vaccine in babies as young as 6 months old. This makes the vaccine by Moderna Canada’s first vaccine against coronavirus for children under 5 years old.
September 8, 2022 Update
- Recently, a preprint of an observational study conducted using a digital platform was published on medRvix. The digitally enabled, at-home study was conducted by Moderna to examine COVID-19 antibody response over time. The study reports that individuals who received two primary Moderna vaccine shots and a Moderna booster shot had longer-lasting antibody levels than those who received Pfizer ones. This observational real-world study is the first of its kind to use a digital platform and consumer-directed technology to assess real-world immunity following COVID-19 vaccination.
- The Medicines and Healthcare Regulatory Agency in the UK gave Moderna’s updated bivalent vaccine the green light to be used as a booster shot, making the British drug regulators the first in the world to approve the updated Moderna coronavirus vaccine. The updated bivalent coronavirus-19 vaccine by Moderna targets the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants, as well as the original COVID-19 strain.
- The Moderna bivalent COVID-19 vaccine is now the first bivalent COVID-19 vaccine approved for use in Australia. On August 29, 2022, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia approved the use of the Moderna bivalent novel coronavirus vaccine as a booster dose in adults aged 18 years and older.
- On August 31, 2022, the FDA authorized the emergency use of the bivalent Covid-19 vaccine booster shots from Moderna in individuals 18 years of age and older. Similar to the Pfizer updated booster, the bivalent Moderna mRNA booster vaccine combines two mRNA components; one against the original COVID strain, and another against the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron sublineages.People will be able to receive the Moderna bivalent vaccine, also called “updated booster”, as a single booster shot at least 2 months after primary or booster vaccination.
- Similarly, The CDC has approved the use of the updated COVID-19 booster from Moderna for individuals aged 18 years and older.
- In the fight against the Omicron variant, Taiwan’s Food and Drug Administration also approved the use of the updated Moderna bivalent vaccine as a booster shot in individuals aged 18 years and older.
- Japanese officials have confirmed the death of a third person following a second Moderna vaccine shot. The 49-year-old man died one day after getting his Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. His only known health problem was an allergy to buckwheat.
December 27, 2022 Update
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared the updated (bivalent) Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for use in children as young as 6 months of age.
- The CDC also announced that children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years can now receive the Moderna bivalent booster shot two months after their final primary series dose.
OXFORD/ASTRAZENECA VACCINE
The Oxford /AstraZeneca was the first traditional vaccine against corona to be approved worldwide. It was well accepted by health authorities, but seems to have slightly less effectiveness compared to the mRNA vaccines (Moderna and Pfizer).
Nevertheless, AstraZeneca was well received and has proven itself as a top vaccine against COVID-19.
Technology and Dosage
The AstraZeneca vaccine, also called Vaxzevria, is produced using a traditional method of vaccine production - it’s what we call a vector-based vaccine.
Scientists at Oxford University have modified the common cold virus (called “adenovirus”) to carry corona’s spike protein. The harmless modified virus “infects” your cells, and presents the spike protein to your immune system.
Immune cells and antibodies will be produced to fight any future infection with COVID-19 shall it occur.
The vaccine is given in 2 doses, 8 to 12 weeks apart. A third booster dose is recommended after 4-6 months.
Health authorities preferentially recommend Moderna or Pfizer booster jabs for those who had received 2 doses of AstraZeneca. Studies have shown that this mixing and matching leads to improved immune response. Nevertheless, you can get a third AstraZeneca shot if you have a medical reason that prevents you from getting an mRNA booster.
Approval
AstraZeneca is approved by the EMA and WHO. Nevertheless, Vaxzevria is still not approved by the FDA to be used in the United States.
The AstraZeneca vaccine is also largely accepted by local health authorities in many countries around the globe.
Effectiveness
The original efficacy studies showed that 2 doses of AstraZeneca were at around 76% against symptomatic illness and 100% against hospitalization and critical illness.
One study, however, showed that the vaccine protection got down to 47% after 5 months of the second jab. This is why a third booster dose is now recommended, as with all other vaccines.
A study showed that a third dose with Pfizer boosts immunity back up to 68%. On the other hand, getting a third AstraZeneca shot led to only 50% protection.
Concerns
The main concern that rose in 2021 regarding AstraZeneca was the claim that it causes blood clots (e.g. deep vein thrombosis - DVT).
Blood clot formation is indeed a side effect of the AstraZeneca vaccine. However, it is extremely rare and does not deserve the hype and fear that broke with the news. According to some estimates, blood clots develop in 4-6 people of every 1 million that get vaccinated. That’s a very low chance of getting a blood clot.
At the beginning of the hype, many countries restricted AstraZeneca to those aged 40, 50, 60, or older. However, now, these recommendations have been lifted. All adults aged 18 and over in countries that approve AstraZeneca can have it.
Age groups
AstraZeneca is not approved for use in children. The EMA and WHO recommend it only in adults aged 18 and older.
An ongoing study by AstraZeneca is assessing the efficacy and safety of the vaccine and will hopefully provide more insight into this age group.
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new trial by AstraZeneca showed that a 3rd shot of the same vaccine provides increased immune response against Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma variants
March 4, 2022 Update
- AstraZeneca combined with a Pfizer second dose led to 89% protection after one month of the vaccination. However, after 6 months, protection dropped to 66%.
- An announcement by AstraZeneca said that the vaccine can be an effective booster against Omicron for those who had been fully vaccinated with Pfizer or Moderna.
- Australian health regulators have approved AstraZeneca as a booster for those who had already been fully vaccinated with an mRNA vaccine.
April 5, 2022 Update
- A study showed that the AstraZeneca vaccine is effective in protecting socially vulnerable populations in Brazil where Gamma and Delta were the dominating strains. The AstraZeneca vaccine was able to protect against symptomatic COVID-19 by 31% after the first dose and 65% following the second.
- The effectiveness of a single dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine was evaluated in a new study and compared to that of the Pfizer vaccine. A single dose of AstraZeneca vaccine reduced hospitalization rates from 18.2 per 1000 person-years in unvaccinated individuals to 15.1 per 1000 persons.
May 6, 2022 Update
- In early May, a case report was published describing the first reported case of ocular myasthenia gravis following vaccination with the Oxford-Astrazeneca Covid-19 vaccine. Ocular myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that can cause weakness in the muscles of the eyes. Researchers believe that this case of ocular myasthenia gravis was induced by the viral vector in the Oxford-Astrazeneca Covid-19 vaccine.
- A recent study compared the effectiveness of two doses of the Oxford-Astrazeneca Covid-19 vaccine with two doses of the mRNA vaccines. The Oxford-Astrazeneca Covid-19 vaccine and the mRNA vaccines were found equally effective in protecting against hospitalization and death from Covid-19 infections.
June 6, 2022 Update
- AstraZeneca’s recombinant Covid-19 vaccine, Vaxzevria, has been approved as a third dose booster in adults. The vaccine has been granted approval in the European Union (EU) by the European Medicine Agency (EMA).
- A recent staff report was released by the House Oversight committee on the coronavirus vaccine manufacturing failures of emergent biosolutions. The report stated that millions of doses of the AstraZeneca Covid-19 vaccine were destroyed due to manufacturing issues at an Emergent Biosolutions plant.
- The ATAGI (Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunization) recently updated its clinical recommendations for Covid-19 vaccines. According to the ATAGI, the AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine may be used as a third dose if there are contradictions to mRNA Covid-19 vaccines.
August 5, 2022 Update
- A recent expert review showed that two doses of AstraZeneca’s Covid-19 vaccine were as effective as mRNA Covid-19 vaccines in protecting people against Covid-19 hospitalization and death.
- A real-world evidence study was done in Northern Thailand to assess the effectiveness of AstraZeneca’s Vaxzevria recombinant Covid-19 vaccine. The authors concluded that a fourth booster dose of the AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine was 73% effective against the Omicron variant.
September 8, 2022 Update
- Japan has approved AstraZeneca’s Evusheld COVID-19 vaccine, earning AstraZeneca its first global approval as a COVID-19 treatment.
- Up to and including 24 August 2022, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the UK received over 200,000 reports of suspected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine. There have also been reports of 444 major cases of blood clots (thromboembolic events) with low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia) in the UK following vaccination with AstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine. However, these suspected ADRs are not “proven side effects” of the coronavirus vaccine by AstraZeneca. *Note that these reported cases are out of 24.9 million first doses and around 25 million second doses of the COVID-19 AstraZeneca vaccines administered in the UK so far.
- AstraZeneca’s CEO told Reuters that the company may stop the production of its COVID-19 vaccinations. This came after production delays by regulators (due to reports of adverse events) and competition with mRNA vaccines.
- A study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases investigated the effectiveness of primary vaccination with the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine compared to Valneva’s inactivated coronavirus vaccine. The participants were individuals aged 18 years or older from 26 sites in the UK. The authors reported that the COVID-19 vaccine by Valneva had a superior immune response to that provided by the AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine.
December 27, 2022 Update
- According to the BBC, a man in the UK died of a blood clot to the brain after receiving the AstraZeneca Covid jab. The coroner reported that the blood clot was the direct result of the AstraZeneca Covid-19 vaccination, which the man received more than a year earlier.
- A team of Australian scientists investigated how AstraZeneca’s vaccine causes blood clots in some rare cases.
Their research revealed that a gene known as IGLV3-21*02 might be responsible for the blood clots. After vaccination, this gene causes the body to produce “rogue” antibodies against the coronavirus. These antibodies can recognize and bind to PF4, a small molecule that can make the blood clot.
In some rare cases, people with the IGLV3-21*02 gene can produce antibodies that activate the PF4 molecule after the AstraZeneca Covid vaccine. The activated PF4 signals the blood to clump together, resulting in a blood clot.
- In December 2022, AstraZeneca launched a Phase III SUPERNOVA clinical trial evaluating its next-generation long-acting antibody combination Covid vaccine, AZD5156. The new investigational vaccine combines EVUSHELD with a new long-acting monoclonal antibody. Early studies show that the AZD5156 vaccine by AstraZeneca can neutralize all known coronavirus variants to date, including the Omicron subvariants.
Sputnik V Vaccine
The Sputnik V, produced by the Gamaleya Institute in Russia, was the first vaccine to be approved in the country. Over the course of the year, Sputnik has proven itself to be safe and effective in protecting against corona infection and severe illness.
Even though studies show a lot of promise with Sputnik V, it is still not one of the WHO-approved vaccines.
Technology and Dosage
The Sputnik V vaccine is vector-based, just like AstraZeneca. It uses a modified version of the adenovirus to reproduce the spike antigen in the body.
Sputnik V is taken in 2 doses, 21 days apart. Alternatively, a 1-dose version of the vaccine is also available, and it’s called Sputnik light.
There’s still no official protocol to determine whether or not a booster is needed after the second dose of Sputnik V. Ongoing studies show that a booster Sputnik light dose can boost immunity against the new Omicron variant, even higher than what could be achieved with mRNA vaccines.
Approval
The Sputnik V is not FDA, EMA, or WHO approved. The WHO has claimed that there are “manufacturing concerns” and “missing documents” that have brought the approval process to be suspended.
However, Sputnik V is approved in several countries like Russia, Mexico, Chile, Columbia, Iran, and others.
Effectiveness
The original study that determined the efficacy of Sputnik V concluded that it is 92% effective in preventing COVID-19. Another newer study done in the UAE found out that the vaccine was 97.8% effective.
As for the single-dose Sputnik light, studies show that it provides 93.5% protection against corona.
Concerns
The WHO has announced that it has concerns about the manufacturing of Sputnik V, however, there’s still no clear answer to what exactly these concerns are.
Age groups
The Russian vaccine is approved for use in Adults. However, health authorities have recently announced that Sputnik will also be available to children and teenagers aged 12-17. Studies are ongoing to determine the safety and efficacy of the Russian vaccine in younger children.
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new study showed that 2 doses of the Sputnik V vaccine lead to the development of two times more neutralizing antibodies against Omicron compared to Pfizer.
- Russian health authorities have granted Sputnik V full and permanent approval in the country.
- Russia is expecting WHO approval for the Sputnik V vaccine in the near future. Despite the lack of WHO approval, Sputnik V is approved in more than 70 countries with a total population of more than 4 billion people.
March 4, 2022 Update
- Sputnik V was approved for adolescents in Kazakhstan, making it only the second country to authorize the vaccine in this age group after Russia.
- Indian health authorities have approved the single-dose Sputnik Light vaccine for emergency use in India.
- A new nationwide Hungarian study showed that Sputnik V provides 98% protection against mortality and 85.7% protection against infection.
April 5, 2022 Update
- A new study published by The Lancet announced that Sputnik V is effective in the immunization against SARS-CoV2 in HIV positive patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- Sputnik V posted on twitter that the Russian Health Ministry has registered the nasal version of Sputnik V, making it the world’s first approved nasal vaccine against COVID-19. The director of the Gamaleya Centre, Alexander Gintsburg, says the nasal vaccine will be effective against the Omicron strain.
May 6, 2022 Update
- According to Reuters, the Philippines has five million doses of the Sputnik V Covid-19 vaccine that are close to expiry. The Philippines is planning on donating these doses to Myanmar.
- A recent study revealed that a second shot of the Moderna vaccines after a first shot of the Sputnik V vaccine was more effective in inducing an immune response than 2 shots of the Sputnik V vaccine.
June 6, 2022 Update
- The World Health Organization (WHO) still has not approved the Sputnik V Covid-19 vaccine.
August 5, 2022 Update
- A recent study published in Nature assessed the effectiveness of the Sputnik V coronavirus vaccine in increasing the immunity against Covid-19. The clinical trial was performed on individuals with or without previous Covid-19 infections in Kazakhstan. There were no reported severe or life-threatening adverse events following 2 doses of the vaccine. Moreover, compared to dose 1, dose 2 did not significantly increase protection against the coronavirus.
September 8, 2022 Update
- In Russia, the Gamaleya National Research Center of Epidemiology and Microbiology announced the development of a new Sputnik V vaccine that specifically targets the Omicron and Delta variants of the novel coronavirus. The GNRCEM stated that the new Sputnik V vaccine was able to reduce the viral load in the lungs of animals infected with the Omicron BA5 variant.
- The Washington Post reported that the new US travel rules allowing fully vaccinated foreign travelers to enter the US starting November will exclude those who have received Russia’s Sputnik V vaccine.
December 27, 2022, Update
- A new study showed that the intranasal Sputnik V Covid vaccine induces a strong and durable immune response in animals. The vaccine was given intranasally to mice and non-human primates (common marmosets). Antibodies were found in their nasal mucosa and blood serum for up to 180 days following intranasal vaccination.
JONHSON & JONHSON
The J&J vaccine is an approved 1-dose vaccine. The vaccine was found to be less protective compared to other COVID vaccines, like Moderna and Pfizer. Nevertheless, the FDA and WHO have determined that the potential benefits are enough to approve it.
Technology and Dosage
The Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID vaccine is produced using the same technology as AstraZeneca and Sputnik V. It’s a vector-based vaccine that uses the adenovirus to introduce the spike protein to the immune system.
The J&J vaccine was the first approved single-dose vaccine against corona. However, a booster dose is now recommended.
The booster dose after Johnson & Johnson is given 2 months after the initial jab. The CDC recommends getting either Pfizer or Moderna as a booster for J&J.
Approval
The Johnson & Johnson single-dose corona vaccine is approved by the FDA, WHO, and EMA.
Effectiveness
A single dose of the Johnson and Johnson vaccine is 66% effective against the original coronavirus. However, with time, the protection decreases to reach a shocking 13% after 6 months of vaccination.
This, and the new Omicron outbreak have made a booster necessary. A new study shows that a booster shot with a second Johnson and Johnson jab increases protection against Omicron back to 85% after 2 months of the shot.
Concerns
News about blood clots after Johnson and Johnson broke in the first half of 2021.
Nevertheless, health authorities have dismissed claims that blood clotting is a common side effect of the vaccine. Today, we know that blood clots are a very rare and treatable condition that can happen after COVID-19 vaccination.
Age groups
The Johnson and Johnson vaccine is approved in adults only (18 and over).
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new study showed that 2 doses of the Johnson and Johnson vaccine reduced hospitalization by 85% compared to only 1 dose. The study was performed during the Omicron surge in South Africa, possibly reflecting effectiveness against this variant.
- A new announcement by the CDC said that mRNA vaccines are “preferred” to Johnson & Johnson if available.
March 4, 2022 Update
- Reports suggest that Johnson & Johnson has suspended the production of their vaccine.
April 5, 2022 Update
- A recent study found that people who received a single J&J shot or a shot and a booster had less protection against severe COVID-19 than people who received two doses and a booster shot of Moderna or Pfizer vaccine.
- The new FDA and CDC authorization of a fourth vaccine shot left out J&J from their recommendations.
May 6, 2022 Update
- Recently, data on the Johnson & Johnson Covid-19 vaccine from the CDC’s Vaccine Safety Datalink was analyzed. The analysis showed that people who received the J&J/Janssen vaccine had a higher risk of developing a rare disorder called Guillain-Barre syndrome than those receiving the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines.
- A new study evaluated the antibody immune response to Covid-19 vaccines in patients with cancer undergoing treatment. The findings showed that the antibody response in these patients was at its highest 2 months after receiving 2 doses of the J&J vaccine.
- The FDA has stated it isis limiting the emergency use authorization of the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Covid-19 vaccine to people 18 and older for whom other vaccines aren't appropriate or accessible and those who opt for J&J because they wouldn't otherwise get vaccinated.
June 6, 2022 Update
- Recently, the FDA has set new restrictions on the use of the Johnson & Johnson Covid-19 vaccine. The FDA has limited the authorized use of the J&J vaccine to individuals 18 years or older for whom other approved vaccines are not available or who choose to receive the J&J vaccine because they would otherwise not accept a Covid-19 vaccination. These limitations came after analyzing report cases that showed a high risk of blood clots two weeks following the administration of the Janssen Covid-19 vaccine.
- According to Reuters, Nigeria has received 4.4 million doses of the J&J coronavirus vaccine from Spain.
August 5, 2022 Update
- South Africa reported a causal link between the Johnson & Johnson’s Covid-19 vaccine and the death of an individual. After being given the J&J Covid-19 vaccine, the person developed the rare Guillain-Barre Syndrome neurological disorder. The person was later put on a ventilator and died. This is the first death that has been causally linked to a Covid-19 vaccine.
- The world health organization (WHO) declared the J&J Covid-19 vaccine safe and effective for all individuals 18 years old and above.
September 8, 2022 Update
- The National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) in Canada approved a booster dose of the Janssen Jcovden COVID-19 vaccine in individuals aged 18 and older who are unable to receive an mRNA vaccine or the Novavax Nuvaxovid vaccine. The Janssen booster dose is to be administered at least 2 months after a primary vaccination series.
SINOPHARM VACCINE
The first Chinese corona vaccine, Sinopharm, is now one of the 10 WHO-approved vaccines.
Technology and Dosage
The Sinopharm vaccine is produced using traditional vaccine-producing technology. Nevertheless, it’s different from the methods used to produce AstraZeneca, J&J, and Sputnik V.
Sinopharm is an inactivated vaccine. This means that the shot contains an inactivated and harmless version of the original coronavirus.
After you receive the vaccine, your body will produce immune cells and antibodies to combat any future corona infections.
The vaccine is given in 2 doses, 21 days apart. A third booster dose with AstraZeneca, Pfizer, or Moderna is recommended.
Approval
Sinopharm is approved by the WHO, but not by the FDA or EMA. It’s currently being administered in China, South America, Central Asia, the UAE, and other countries around the world.
Effectiveness
According to the original Phase III trial, the Sinopharm vaccine is 79% effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 symptoms.
A booster dose of Sinopharm, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, or Moderna can be given to boost immunity after 6 months of the second dose.
Sinopharm recently announced a new protein-based booster shot that provided a “stronger immune response” against Omicron. Sinopharm's “NVSI-06-07” booster has been authorized for emergency use by health authorities in the UAE.
Age groups
Sinopharm is approved for adults (18 plus) and children above 3 years of age in specific countries like the UAE and China.
February 11, 2022 Update
- Health authorities in Abu Dhabi have made a 4th booster shot of Sinopharm or Pfizer available to those who had already had 3 shots of Sinopharm.
March 4, 2022 Update
- Sinopharm vaccination certificate is now accepted for travel in 16 out of 27 EU member states.
- A new study found that immunity goes down after 3 doses of Sinopharm, and a 4th booster dose with the same vaccine does not significantly restore it.
April 5, 2022 Update
- Sinopharm officially started the production of its COVID-19 vaccine in Myanmar according to the Global Times. The Myanmar factory will be the first Sinopharm factory in Southeast Asia.
May 6, 2022 Update
- According to Reuters, the world’s first inactivated vaccine candidate against Omicron, developed by Sinopharm and Sinovac Biotech, has been cleared for clinical trials in Hong Kong.
June 6, 2022 Update
- Recently, Sinopharm and the University of Hong Kong (UHK) launched a new clinical trial for a Covid-19 vaccine targeting the Omicron variant. The research teams hope that the new vaccine would be ready for the public by November, 2022.
August 5, 2022 Update
- The interim recommendations for using the Sinopharm Covid-19 vaccine were reconfirmed by SAGE; the world health organizatiton’s strategic advisory group of experts (SAGE) on immunization.
September 8, 2022 Update
- A cohort study done in Singapore investigated the level of protection offered by 3 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines compared to 3 doses of inactivated Sinopharm SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. The research revealed that 3 doses of the Sinopharm coronavirus vaccine offered greater protection than 2 doses. However, the protection offered by the 3-dose Sinopharm vaccine was weaker than that offered by 3-dose mRNA coronavirus vaccines.
- Sinopharm plans on starting clinical trials for an Omicron-specific mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. The Chinese vaccine producer, Sinopharm, has submitted its application for clinical trials of a domestic mRNA COVID-19 vaccine that targets the Omicron variant specifically and is waiting for approval.
Other Vaccines
In addition to the most famous vaccines mentioned above, there are several other COVID-19 vaccines currently being administered all around the world.
CORONAVAC
Sinovac is a Chinese inactivated virus, similar to the Sinopharm vaccine. The vaccine is approved by the WHO for use in adults. It’s given in 2 doses, 2 weeks apart.
A large Brazilian trial found that Coronavac was 51% protective against corona infection and 100% protective against severe symptoms and hospitalization.
The WHO currently does not recommend the vaccine in children, however, certain countries have authorized the vaccine in kids aged 3 years and up. This comes after a large trial showed that the Sinovac vaccine was safe and effective in children in this age group.
The WHO recommends mixing and matching with a booster dose from another class (e.g. Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca) to achieve the highest level of protection possible.
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new study from Yale found that mixing CoronaVac with a 3rd Pfizer booster dose lead to an increase in Omicron-neutralizing antibodies.
- Another study found that 3 doses of CoronaVac produced increased antibody response against variants of concern, including Omicron
March 4, 2022 Update
- Sinovac’s CEO has announced that a booster specifically designed against Omicron is currently in development.
April 5, 2022 Update
- According to Reuters, a study in Chile, which hasn’t yet been peer reviewed, showed that the Sinovac vaccine was effective in preventing COVID infections in 38% of children aged 3 to 5.
May 6, 2022 Update
- A study recently published in The Lancet Global Health, researchers investigated the effectiveness of the Coronavac vaccine booster doses against Covid-19 infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and deaths. The study results showed that a booster (third) dose of the Coronavac vaccine, or using a different booster vaccine such as Pfizer or Astrazeneca, following 2 doses of the same vaccine was effective in protecting against Covid-19 infections, hospitalization, and related deaths.
- Another recent study revealed that one or two doses of Coronavac can provide protection against the Omicron variant among recovered Covid-19 patients.
- According to Folha De S.Paulo, Brazil’s minister of Health, Marcelo Queiroga, announced that the Coronavac vaccine will be restricted to children and adolescents between the ages of 5 and 18. Brazil’s ministry of health worries that there still isn’t enough evidence supporting the use of the Coronavac vaccine for people older than 18 years old.
June 6, 2022 Update
- A new study investigated the efficacy of the Coronavac and Pfizer-BioNTech Covid-19 vaccines in patients with cancer. The study showed that two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vaccine and 3 doses of the CoronaVac vaccine were equally efficient in protecting cancer patients against the novel coronavirus.
August 5, 2022 Update
- Sinovac announced that its CoronaVac Covid-19 vaccine has been approved for use in children aged 6 months through 3 years in Hong Kong, China. The vaccine will be given in a series of 3 doses; the first two doses 28 days apart, followed by a third dose at least 3 months after the second dose.
- The Chinese Sinovac Covid-19 vaccine has been also approved for emergency use in children aged 3 to 5 years old in Brazil.
- In a recent study, a group of scientists from Thailand showed that a booster shot of the Pfizer mRNA Covid-19 vaccine provided the same level of immunity against Covid-19 to people whose first two shots were either an mRNA or the Sinovac vaccine.
September 8, 2022 Update
- A cohort study published in JAMA Infectious Diseases studied the effectiveness of a booster mRNA vaccine against severe COVID-19, compared to the effectiveness of a 3-dose Sinovac booster. The authors found that 3 doses of the Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine were more effective in protecting against the coronavirus than 2 doses. However, 3 doses of mRNA vaccines offered more protection against COVID-19 than 3 doses of the Sinovac vaccine.
- A national-wide study was done on around 14 million individuals in Malaysia who received a booster shot of either the Sinovac or Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine after primary vaccination. The study concluded that the Pfizer booster shot may offer stronger protection against the coronavirus than the Sinovac booster shot.
- Sinovac was recently approved by the Chilean Public Health Institute to start phase 2 clinical trials for 2 new COVID-19 vaccines. The first is an inactivated Omicron strain COVID-19 vaccine, and the second is a trivalent COVID-19 vaccine (against ancestral, delta, and Omicron variants). The clinical trial will assess the safety and immunogenicity of one booster dose of the two candidate vaccines. This will be the first study researching a multivalent inactivated coronavirus vaccine.
December 27, 2022, Update
- A new study in the Clinics journal showed that the CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine by Sinovac is extremely safe in people with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AVV). However, the vaccine generates only a moderate immune response against the coronavirus. The scientists also noted that a CoronaVac booster shot, given 6 months after the first dose, increases the immune response.
- According to a letter published in the Annals of Oncology, COVID-19 vaccination might improve a patient’s response to nasopharyngeal cancer treatment. Patients with nasopharyngeal cancer vaccinated with CoronaVac responded better to anti-PD-1 therapy and chemotherapy than those who were unvaccinated.
- Scientists revealed that the Pfizer and CoronaVac vaccines are less effective in protecting people against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant XBB sublineage, a BA.2.10.1–BA.2.75 recombinant.
- However, a recent study published in The Lancet verified that a booster shot of either the Pfizer (BNT162b2) or CoronaVac vaccine protects people against Omicron BA.2 infection and symptomatic covid infection effectively.
- According to the Global Times, a phase 1/2 clinical trial showed that the CoronaVac vaccine was safe for healthy seniors aged 60 and over. There weren’t any reported serious side effects or adverse reactions.
COVISHIELD
Covishield is an Indian version of the AstraZeneca vaccine. It is the same vaccine, however, it’s locally produced by the Serum Institute of India. It’s given in 2 doses, 8 to 12 weeks apart. The vaccine is approved by the WHO.
The original efficacy studies showed that Covishield is 62% effective in preventing COVID-19. Newer studies during the Delta variant outbreak in India showed that the vaccine remained protective and prevented death in 91% of infected cases.
Health authorities have determined that the booster shot should be with the same Covishield vaccine in those who got their first 2 shots.
Covishield is approved in adults only, but not in children and teenagers.
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new study found that a 3rd booster dose with Covishield or an mRNA or Inactivated vaccine leads to an increased immune response against Omicron.
April 5, 2022 Update
- The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI) in India recommended decreasing the gap between the first and second Covishield doses from 12-16 weeks to 8-16 weeks.
May 6, 2022 Update
- A new study investigated the risk of adverse events, including headaches, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and chills, following vaccination with Covishield. The study concluded that these vaccination-associated side effects were mild and easily manageable after vaccination with Covishield.
- According to news sources, the National Institute of Virology (NIV) in Pune, India reported a case of 3-time Covid infection in a person vaccinated with two doses of the Covishield vaccine. However, the patient experienced mild symptoms during his second and third Covid-19 infections.
June 6, 2022 Update
- A new case report was published on acute myocardial infarction after Covid-19 vaccination. A 68-year old male presented with myocardial infarction within 12 hours after taking the Covishield vaccine.
- 15 EU countries, including Germany, now recognize Covishield vaccine for travel. This makes the Covishield coronavirus vaccine the 5th vaccine recognized for travel by Germany along the BioNTech/Pfizer, Janssen, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines.
August 5, 2022 Update
- A recent Indian study published in the Journal of the Association of Physicians of India (JAPI) compared the adverse events (malaise, fever, bodyaches, headaches, etc) in patients following the Covishield vaccine and the Covaxin vaccine. The results of the study showed that a higher number of patients experienced adverse events after the Covishield vaccine than the Covaxin one.
September 8, 2022 Update
- In a recent study, a team of Indian fertility researchers investigated the effect of the Covishield COVID-19 vaccine on male fertility. The results of the study were published in the Official Journal of Society for Reproduction and Fertility. The results of the study confirmed that the Covishield vaccine does not cause changes in semen quality and does not harm male fertility.
December 27, 2022, Update
- A scientific study showed that Corbevax, a peptide-based vaccine, as a booster maximizes protection against covid in people vaccinated with 2 doses of Covishield. When combined with Covishield, the heterologous vaccine booster Corbevax also increased immunity against the Omicron variants.
COVAXIN
Covaxin is the second Indian vaccine against corona to be approved. It’s an inactivated vaccine, similar to the Chinese Sinopharm vaccine. It’s given in 2 spaced doses. It’s also approved by the WHO, but not the FDA or EMA.
The original Phase III trial announced 77.8% effectiveness of Covaxin against the coronavirus.
Indian authorities have determined that the 3rd booster dose should be with the same Covaxin in those who already had 2 jabs.
The Covaxin is currently only approved in adults.
February 11, 2022 Update
- Bharat Biotech has announced a new intranasal vaccine, called BBV154. The novel vaccine is being studied as a possible booster for Covaxin and Covishield.
April 5, 2022 Update
- WHO interim recommendations on Covaxin vaccine have been updated. WHO recommends a Covaxin booster shot 4-6 months after the first dose.
May 6, 2022 Update
- WHO has recently suspended the supply of Covaxin vaccine through UN agencies. This decision came after a WHO inspection of the Bharat Biotech manufacturing facilities in March 2022. The inspection identified deficiencies in good manufacturing practices (GMP). The Bharat Biotech company announced that it will suspend Covaxin production for export while they develop corrective measurements. As a result, Covaxin supply will be interrupted for the foreseeable future.
- Meanwhile, Bharat Biotech is still seeking approval from the Drug Controller General of India for a booster dosage trial of the Covaxin vaccine in people under the age of 18 years old.
- The Drug Controller General of India has approved emergency use of the Covaxin vaccine in children aged 6 to 12 years.
June 6, 2022 Update
- The FDA has lifted the hold on phase 2/3 clinical trials for the Covaxin vaccine according to a press release made by Ocugen Inc, Bharat Biotech’s partner for the vaccine in USA and Canada.
- According to news sources, the phase3 trial for Bharat Biotech Covaxin vaccine has been successfully concluded at AMU.
August 5, 2022 Update
- The interim recommendations for using Bharat’s Covaxin Covid-19 vaccine were reconfirmed by SAGE; the world health organizatiton’s strategic advisory group of experts (SAGE) on immunization. A booster dose may be offered to high-risk groups (older adults, health workers, people with comorbidities) 4-6 months after the second shot.
September 8, 2022 Update
- Bharat Biotech’s first intranasal COVID-19 vaccine, iNCOVACC (BBV154), received approval in India for emergency use in individuals 18 years and older. The intranasal vaccine by Bharat was found safe, well-tolerated, and immunogenic in controlled clinical trials. The iNCOVACC intranasal vaccine, a recombinant replication-deficient adenovirus vector vaccine, is administered as drops in the nose.
December 27, 2022, Update
- India’s Union Health Ministry approved Bharat Biotech’s intranasal Covid-19 vaccine, iNCOVACC, as a booster dose for people 18 years of age and older. Adults previously vaccinated with two doses of either Covaxin or Covishield can now receive the needleless iNCOVACC intranasal vaccine as a booster dose.
NOVAVAX
Novavax, one of the latest WHO-approved vaccines, is somewhat of a latecomer to the market. It’s also been recently approved by the EMA for use in Europe. The vaccine uses a unique technology compared to other corona vaccines.
Novavax is a subunit vaccine. This means that it’s made of a protein that mimics the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. It’s easier to mass-produce compared to traditional vaccines, giving Novavax a possible advantage in the future.
The Novavax vaccine was shown to be 90.4% protective against the coronavirus. The vaccine is thought to be effective against different variants, however, more studies need to confirm efficacy against Omicron in particular.
Currently, Novavax is given in two doses, 3-4 weeks apart. A third booster dose of Novavax is recommended in immunocompromised patients.
Novavax is only approved in adults so far.
An Indian version of Novavax, called Covovax, has also been approved by the WHO.
February 11, 2022 Update
- UK health authorities have approved Novavax, making it the fifth approved corona vaccine in the kingdom.
- German health authorities have also approved Novavax, but recommend mRNA vaccines as a boosters
- Novavax is currently testing its vaccine in children aged 12 to 17. However, the company has future plans to extend their testing to include children as young as 6 months.
March 4, 2022 Update
- A new phase III trial showed that Novavax protection is maintained at 82.5% after 6 months of full vaccination.
- Novavax has announced that their vaccine is 80% effective in children aged 12 to 17 years.
- Australia has approved Novavax as a booster shot for those already fully vaccinated.
- Although a latecomer, Novavax is being widely endorsed by healthcare authorities all over the world, climbing the ladder up to be compared with Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca. It has already been approved in countries like Canada, the USA, Germany, the UK, and Australia.
April 5, 2022 Update
- Novavax has asked to expand the authorization of its vaccine in the European Union to include adolescents aged 12-17.
- The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine has arrived in Canada and it is the only protein-based COVID-19 vaccine approved by Health Canada. The vaccine is to be administered to individuals 18 years and above.
- The Novavax vaccine is now included in two booster trials. The results of these trials will help determine whether Novavax can be used as a booster after primary immunization with an FDA approved vaccine.
May 6, 2022 Update
- Novavax is seeking FDA approval for the use of the vaccine in adults 18 years of age and older. The FDA committee will review Novavax’s request in early June.
- The first Novavax shipment has arrived in Singapore. The vaccine doses will be administered starting from the end of May.
- Novavax announced that its combination vaccine targeting both the Covid and Flu viruses showed promising results in early data.
- Novavax has started phase 3 clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of a booster (third) doseof its protein-based vaccine among children aged 12-17 years.
- The FDA still hasn’t approved the emergency use of Novavax in the USA.
June 7, 2022 Update
- An FDA committee will meet today, on June 7 2022, to discuss the request for the authorization of the emergency use of the Novavax coronavirus vaccine in individuals 18 years of age and older.
August 5, 2022 Update
- The CDC now recommends Novavax’s Covid-19 vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older thus adding the protein-based Novavax vaccine to the list of coronavirus vaccines available for adults in the USA. The CDC hopes that this more traditional vaccine will encourage more adults to get vaccinated against Covid-19 in America.
- The county of Santa Clara in Northern California has already started administering the Novavax Covid-19 vaccine at all County Health System vaccination sites. The vaccine is administered in 2 doses given 3-8 weeks apart.
- The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has extended the use of Novavax’s Covid-19 vaccine, Nuvaxovid, in adolescents aged 12 through 17 years old.
- According to Reuters, the European Medicines Ageny (EMA) now recommends that the Novavax’s Covid-19 vaccine must carry a warning of the possible heart side effects (two types of heart inflammation).
September 8, 2022 Update
- The FDA updated its Emergency Use Authorization for the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine to include individuals aged 12 years and older. The Novavax coronavirus vaccine was previously approved for individuals 18 years and older.
- Britain’s medicines regulators have also extended their approval of the use of Novavax’s protein-based COVID-19 vaccine to include adolescents between the ages of 12 and 17 years. Switzerland also approved the use of the new Novavax vaccine as a primary vaccine for young people aged 12 years and older, and as a booster shot for people 18 years and older.
- The US Department of Defense has added the newly-approved Novavax to its available COVID-19 vaccinations. Service members now have the option to choose Novavax along with Moderna, Pfizer, and J&J vaccines.
- EU regulators have recommended the use of the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (Nuvaxovid) as a booster shot in individuals aged 18 and older.
- Novavax submitted an application to the FDA for the Emergency Use Authorization of its protein-based vaccine as a booster shot in adults. The company is still waiting for the FDA’s decision.
- A small number of myocarditis and pericarditis cases have been reported within 14 days after vaccination with Novavax’s Nuvaxovid COVID-19 vaccine. However, these are still considered rare side effects of the vaccine.
- A German study investigated the immunogenicity of the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine. Researchers were able to show that the Novavax protein-based vaccine was able to produce an immune response in recipients. Nonetheless, that immune response was weaker than in people who receive mRNA-based coronavirus vaccines.
December 27, 2022, Update
- According to sources, Novavax has applied to the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) to allow its Nuvaxovid vaccine as a booster shot following primary vaccination with either Covishield or Covaxin.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued an updated Emergency Use Listing (EUL) for Nuvaxovid by Novavax. The vaccine has been authorized for use as a primary series of two doses in adolescents aged 12 through 17 and as a booster in adults aged 18 and older.
- Reuters reported that Novavax will start manufacturing its Covid-19 vaccine in Canada by early 2023 after the country’s health regulators have authorized its use as a primary series of two doses in adolescents aged 12 through 17.
CONVIDECIA
A new Chinese vaccine has recently been approved for public use in China. This vaccine is, like J&J’s, a single-dose vaccine, and it’s an adenovirus-based viral vector vaccine, similar to Sputnik V. CanSinoBIO’s vaccine has shown 66% efficacy in preventing COVID symptoms and 91% in preventing severe disease. No serious blood clot cases had been reported in people inoculated with its single-dose COVID-19 vaccine. CanSinoBIO’s vaccine is approved in China, Hungary, Chile, and Pakistan.
According to news reports, CanSinoBio’s phase 1 clinical trial for the first aerosolized inhalable adenovirus type-5 vector-based COVID-19 vaccine (Ad5-nCoV) has shown strong IgG and neutralizing antibody responses.
A small trial from the company indicates that the CanSinoBIO’s single-dose vaccine is safe and effective in children ages 6 to 17. The vaccine was tested at a lower dosage than those given to adults.\
April 5, 2022 Update
- According to a recent study, the intramuscular injection or inhalation of CanSinoBio’s vaccine as a heterologous booster following immunizatoion with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine has a potent antibody response against the Omicron variant.
- CanSinoBio announced that its recombinant vaccine has been approved for usage in Malaysia and Indonesia as a heterologous booster after primary immunization by other vaccines.
May 6, 2022 Update
- According to reports, CanSino Biotech is looking to start its anti-Covid 19 vaccine production in Argentina.
- CanSinoBio’s mRNA-based Covid-19 vaccine candidate was approved to enter clinical trials by the medical product regulator of China, according to Reuters.
June 6, 2022 Update
- Recently, the World Health Organization has granted CanSinoBio’s coronavirus vaccine, Convidecia, Emergency Use Listing.
- A new study assessed the adverse effects following Covid-19 vaccination in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Different Covid-19 vaccines, including the CanSinoBio vaccine, were found to be safe in this population of patients.
September 8, 2022 Update
- The National Medical Products Administration of China (“NMPA”) granted CanSinoBio approval for the use of its recombinant inhaled COVID-19 vaccine as a booster dose. China’s new coronavirus vaccine is inhaled through the nose and mouth in aerosol form. This vaccine works by building mucosal immunity to prevent the COVID-19 virus from entering the body through the nose or throat.
December 27, 2022, Update
- China has been encouraging citizens, especially older ones, to become vaccinated with its latest Covid-19 inhaled vaccine since it’s easy to take, doesn’t hurt, and is effective.
ZAFIVAX (ZF2001)
The fifth and latest Chinese vaccine to be approved is the one developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical Co. Ltd. and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is a sub-unit vaccine, similar to Novavax. Phase III trials are currently underway in several countries around the globe. The manufacturer says that the vaccine is safe and effective against COVID-19, however, there is no public data to confirm this yet.
Although the Anhui Zhifei Longcom vaccine offers the convenience of regular refrigeration storage, it has a major downside: a three-dose regimen. Receivers will have to take 3 shots with a month between doses.
May 6, 2022 Update
- Zifivax has up to date conducted 5 phase 3 trials and received authorization in 4 countries (China, Columbia, Indonesia, and Uzbekistan).
June 6, 2022 Update
- A recent article published in the New England Journal of Medicine assessed the efficacy and safety of the Zifivax coronavirus vaccine in adults. According to the article, the phase 3 clinical trial revealed that the Zifivax Covid-19 vaccine was safe and effective in protecting against symptomatic and severe-to-critical coronavirus cases for at least 6 months after full vaccination.
December 27, 2022, Update
- According to local media, the Jakarta Health Office has resumed vaccination to provide people with third and fourth doses of Pfizer and ZifiVax Covid-19 vaccines.
- ZifiVax has so far conducted six phase-3 clinical trials and received authorization in Columbia, Indonesia, Uzbekistan, and China.
CADILA INTRANASAL VACCINE
As of late August 2021, Indian drug regulators are recommending emergency use approval for a new needle-free vaccine by the local pharmaceutical company, Zydus Cadila.
The Cadila COVID-19 vaccine is the first and only non-injectable COVID vaccine worldwide to reach final stages of testing.
The vaccine is intranasal, which means it is sprayed inside the nose. It’s administered in 3 separate doses.
The recommendation comes after positive results from a phase III trials involving 28,000 participants were published. Researchers found that the vaccine had 66.6% efficacy against COVID-19.
Whether the needle-free COVID vaccine will be approved or not is a question of time.
COVAX - 19
This new Australian corona vaccine is still not approved, however, it’s worth giving an honorable mention.
The vaccine was originally developed by South Australia’s Flinders University. The group of researchers released a peer-reviewed article in August 2021 showing some promising results.
The Australian COVAX-19 vaccine is a recombinant protein-based vaccine, which means that it’s basically a synthetic protein that looks like the COVID-19 spike protein. It trains the immune system to recognize and attack the real virus.
The recombinant protein vaccine was created in cultured insect cells. It is later combined with an adjuvant to further stimulate the immune system.
Testing is still in the early stages, however, researchers were able to detect a meaningful immune response against the coronavirus in animal models. This might translate into another effective coronavirus vaccine by the end of 2021. Moreover, the study group expects that the Australian COVID vaccine will also reduce the rate of transmission, not just illness. Human testing is underway, and the results seem to be promising.
MIXING AND MATCHING COVID-19 VACCINES
Can you take different types of COVID vaccines? Can you mix them? Many studies are currently underway to determine if we can use different types of vaccines for the first and second doses.
Recent data released by Oxford researchers suggest that mixing AstraZeneca with Pfizer/BioNtech produces a “robust immune response”. The response was observed to be stronger when the AstraZeneca jab was given as the first dose, followed by
Pfizer compared to when Pfizer is given as the first shot.
The German Chancellor, Angela Merkel, had received the first shot of AstraZeneca, followed by a second shot of Moderna to encourage mixing and matching efforts.
A combination of Sputnik V and AstraZeneca is currently being tested in several countries like Azerbaijan, the United Arab Emirates, and Belarus. Results are expected to follow in the next few months.
In the UAE, health authorities are already offering an extra Pfizer shot to those who already got 2 doses of the Sinopharm vaccine.
The combination of vaccines could provide broader and longer-lasting immunity against the virus and its new variants. It may also offer greater flexibility in vaccine deployment.
February 11, 2022 Update
- A new large study in India is testing different combinations of Covishield, Covaxin, and the new intranasal BBV154 corona vaccine. Researchers are trying to find the best combination of COVID-19 vaccines that produces the highest levels of protection.
December 27, 2022 Update
- According to experts, mixing different vaccines, such as mRNA-based (Pfizer) and vector-based (Covishield) vaccines can result in a better immune response against Covid-19. One study showed that a booster dose with the peptide-based Corbevax vaccine following primary vaccination with the vector-based Covishield vaccine improves protection against the novel coronavirus. Another study reported that a CoronaVac booster shot after two doses of the mRNA Pfizer vaccine was effective in protecting people against Omicron infections.
Is a booster shot necessary? When will the booster shot be given?
Today, it seems that a corona booster shot is indeed necessary after 6-12 months of receiving the second jab.
Recently published studies have found that vaccine protection against corona significantly wanes with time, reaching below 50% protection after 6 months in some cases (detailed in the next section).
This has pushed most countries to start offering booster vaccines, usually with an mRNA vaccine like Moderna or Pfizer/BioNTech.
AstraZeneca booster shots have already proved effective in boosting immunity when given after 6 months of the second jab. Sinopharm and Pfizer booster shots are already available to all previously fully vaccinated citizens in UAE after 6 months of their second dose. In Germany, all adult citizens are now eligible for an mRNA booster shot, as long as 6 months have passed on the 2nd shot, regardless of the type of the first vaccine.
In light of the data that show waning immunity without a booster jab, European regulators are proposing to restrict travel for those vaccinated more than 9 months ago and have not received a booster dose. If this is approved, you might not be able to travel in Europe without getting your booster covid shot.
Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness with Time
Ever since we started vaccination against corona, people have been asking how long will the vaccine remain protective. Does the effectiveness wane out with time? Will we always need a booster shot after 6 months? After 1 year? Every year?
Several studies have attempted to answer the question of how long COVID-19 vaccines stay effective and how long they protect against the virus.
One study found that the effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine is reduced by 57% after 6 months of vaccination. Older patients (>65 years) and men were found to have lower antibody titers compared to younger patients and women respectively.
Another study tested the waning vaccine protection with time in veterans who had received Pfizer, Moderna, or Johnson & Johnson. The results showed that, after 6 months, Pfizer protection dropped from 87% to 45%, Moderna from 89% to 58%, and Johnson & Johnson dropped from 86% to a shocking 13%.
A preprint study measured the waning immunity after the second dose of AstraZeneca’s vaccine. Researchers estimated that the protection falls to 47% after 5 months of vaccination.
These results show that the antibody titers and hence the vaccine protection indeed reduce with time, further supporting the need for a booster dose.
Studies Comparing Different Vaccines
A new study comparing different corona vaccines was recently published by Hungarian researchers in the Clinical Microbiology and Infection medical journal.
The researchers compared the efficacy of five different covid vaccine types - Moderna, Pfizer, Sputnik V, AstraZeneca, and Sinopharm. The study reviewed data from 3.7 million vaccinated patients since early 2021. Two endpoints were compared: protection against infection and protection against death.
Pfizer/BioNTech was found to be 83.3% effective against infection. This is slightly less than the protection provided by Moderna and Sputnik V, with 88.7% and 85.7% effectiveness respectively. AstraZeneca and Sinopharm fell a bit short compared to other corona vaccines, with 71.5% and 68% effectiveness against infection respectively.
All vaccines seemed comparable in terms of protection against death, with numbers ranging between 87.8% and 97.5% for the 5 different variants.
How effective are the vaccines against new delta variants?
The Delta (1.617.2) variant was first detected in India in December 2020. Since then it has spread very fast to become the most dominant variant in the UK and India. Experts expect that the delta variant will be dominant globally, after reports of outbreaks from all around the world.
The problem is that the delta variant is extremely contagious and spreads much faster than the original coronavirus strain. Authorities also fear that available vaccines and treatments might not be as effective against the new variant.
So far, the vaccines that seem to be effective against the new delta variant include:
- Pfizer/BioNtech
- Oxford/AstraZeneca and Covishield
- Novavax
- Johnson & Johnson
The results are still early in most cases and more testing is needed to confirm them.
How Effective Are The Vaccines Against New Omicron Variant?
As of November 2021, a new concerning coronavirus variant has been discovered in South Africa, and detected in several other countries around the world.
The new South African COVID variant, B.1.1.529, was given the Greek name “Omicron”, as the WHO decided to skip 2 possibly confusing Greek alphabets - Nu and Xi.
So far, from what we know, the Omicron corona variant seems to be more infectious and spreads more quickly compared to older variants. However, there is still no data about whether Omicron is more deadly or more dangerous than other corona variants.
Even though Omicron might not be more deadly, being more infectious means more people would be infected. This will increase the global number of deaths, prolong the pandemic, and possibly give rise to new mutations. So, do the current vaccines work against Omicron?
At this moment, nobody knows for sure. However, most reports from health officials and virologists seem to agree that the vaccines protect against the omicron variant as well.
Most vaccine producers, like Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Moderna, and Johnson & Johnson have announced that they will be heavily investigating the new South African Omicron variant. Some have claimed to be able to produce a new adapted vaccine, specifically to cover Omicron, in just 6 weeks.
In any case, future studies will surely show if the vaccines are indeed effective against the new corona variant or not.
February 11, 2022 Update
- Pfizer and Moderna have already announced that they are planning to design an Omicron-specific vaccine
- A new study showed that a Pfizer and Moderna 3rd booster shot was 90% effective against Omicron
- A booster Sputnik light dose after Sputnik V was found to boost immunity against the new Omicron variant, even higher than what could be achieved with mRNA vaccines.
- A new study showed that 2 doses of the Sputnik V vaccine lead to the development of two times more neutralizing antibodies against Omicron compared to Pfizer.
- Sinopharm recently announced a new protein-based booster shot that provided a “stronger immune response” against Omicron
- One study found that 3 doses of CoronaVac produced increased antibody response against variants of concern, including Omicron
April 15, 2022 Update
- A study published in The Lancet showed that a booster shot of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine offers more than 70% protection against severe Omicron infections.
May 15, 2022 Update
- An article published in Nature Communications concluded that a booster shot of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine can increase protection against the Omicron COVID-19 virus in individuals vaccinated with inactivated vaccines.
August 5, 2022 Update
- In a recent study, scientists showed that a fourth dose of an mRNA vaccine was effective in protecting against symptomatic infection and severe disease from an Omicron infection.
- Moderna has shared the preliminary data analysis of its new bivalent booster vaccine targeting specifically the Omicron variant. The new Moderna booster shot was found effective in protecting against the Omicron coronavirus variant.
September 8, 2022 Update
- A recent study published in The Lancet Rheumatology investigated the effectiveness of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron infections in patients taking immunosuppressant medications. The research revealed that the two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines were effective in protecting immunocompromised patients against infections with the Omicron variant of the coronavirus.
Should I Do An Antibody Test After My Vaccine?
Currently, health authorities do not recommend getting an antibody test after being vaccinated. Many people believe that by doing this, they can confirm whether they are immune or not, however, this isn’t true.
Although it is likely for a positive antibody test to imply immunity, and a negative test to imply the lack of it, there is still no clear data to support this, according to the CDC.
Moreover, some antibody tests do not detect specific immunogenic antibodies, and as such, their results cannot be used to assume the presence or absence of immunity. There is still also no clear relationship to suggest that higher titers of antibodies mean higher immunity.
However, some people still might want to get an antibody test and therefore they are offered at various hospitals worldwide. It is best to talk to your doctor with help understanding the results.
Which Is The Best Corona Vaccine?
There’s no “best vaccine” against corona. The WHO has approved 10 corona vaccines so far to provide access to protection to citizens all around the globe. Any available vaccine is a good vaccine.
The efficacy rate may differ between vaccines, and some might have slightly more annoying side effects than others. Nevertheless, all of the approved vaccines are protective and safe. Any vaccine will help halt the pandemic and protect you from unfavorable outcomes, regardless of the numbers.
Ending the pandemic is a global team effort - every person should take part to break the chain of infectivity and prevent new variants from arising.
To Be Or Not To Be Vaccinated
Every single health authority around the world recommends that you get vaccinated to protect yourself, break the chain of infectivity, and prevent new mutants from developing.
As extensively reported and explained in this article, three things we know for sure:
- The approved COVID-19 vaccines are safe
- The approved COVID-19 vaccines are effective
- The approved COVID-19 vaccines are necessary
This is especially true with the spread of the delta variant which spreads 50% more rapidly compared to other variants. To put things into perspective and highlight how important it is to get vaccinated, here’s how vaccinated and unvaccinated people compare in terms of hospitalization and death:
- French health authorities reported that up to 96% of new cases in France are unvaccinated after a new delta variant outbreak.
- A recent analysis showed that up to 99% of new hospitalizations in the US are unvaccinated individuals. Similarly, up to 99% of deaths from COVID-19 infections in the US are now in unvaccinated people.
- Another analysis showed that a vaccinated 80-year-old patient is as likely as a non-vaccinated 50-year-old patient to survive the infection.
If you’re not already vaccinated, take the first chance you get. The best COVID-19 vaccine is the one that is available to you the soonest.
To search for Healthcare Providers in India providing COVID-19 Vaccine, please click here.
To search for Healthcare Providers in Malaysia providing COVID-19 Vaccine, please click here.
To search for Healthcare Providers in Poland providing COVID-19 Vaccine, please click here.
To search for Healthcare Providers in Thailand providing COVID-19 Vaccine, please click here.
To search for Healthcare Providers in UAE providing COVID-19 Vaccine, please click here.
To search for the best healthcare providers worldwide, please use the Mya Care search engine.
Dr. Mersad is a medical doctor, author, and editor based in Germany. He has managed to publish several research papers early in his career. He is passionate about spreading medical knowledge. Thus, he spends a big portion of his time writing educational articles for everyone to learn.
Sources:
Featured Blogs



