Gynecomastia: Surgical Options for Male Breast Reduction, What to Expect

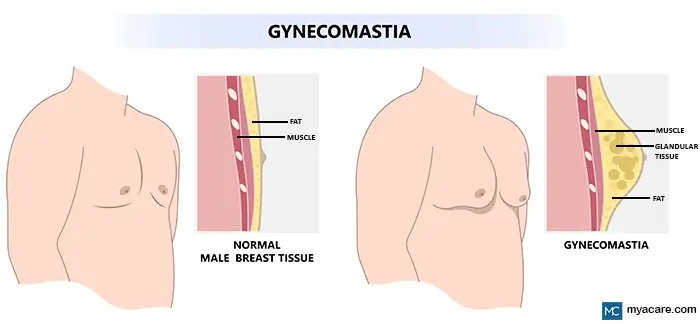
Male breast reduction, or gynecomastia surgery as it is otherwise known, is a procedure for reducing the size of overdeveloped or enlarged breasts in men. This condition is caused by various factors such as hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and genetics.
Gynecomastia is the most prevalent benign breast condition affecting males, primarily those between 50 to 69 years of age. Benign proliferation of glandular breast tissue can also occur in newborn babies, adolescents going through puberty, and men who are obese.
There are several treatment options, including medications and hormonal therapy. However, the combination of surgery and liposuction is currently the most effective method, especially in severe cases of gynecomastia.
Causes of Gynecomastia
An imbalance of hormones, specifically an increase in the level of estrogen, is one of the most common causes of gynecomastia (excessive growth of breast tissue). This can occur naturally during puberty or duet to certain medical conditions. Certain medications can also contribute to the development of gynecomastia. In some cases, the condition may be inherited.
Here are more details about the potential causes of gynecomastia:
1. Hormonal imbalances
Elevated levels of estrogen (the primary female sex hormone) relative to testosterone (the primary male sex hormone) can lead to the development of breast tissue in men. This can occur naturally during puberty, as well as in older men, due to a decrease in testosterone production with age. Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease and tumors of the testicles, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland, can also lead to hormonal imbalances.
2. Medications
Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antibiotics, and heart medications, can lead to gynecomastia as a side effect.
3. Substance abuse
The use of alcohol and anabolic steroids, and certain drugs can also cause gynecomastia.
4. Obesity
Being overweight or obese can increase overall body fat and, in turn, breast tissue.
5. Genetic conditions
Some genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome, can also lead to gynecomastia.
6. Idiopathic
The cause of gynecomastia is unknown in certain cases, which is referred to as idiopathic gynecomastia.
It is important to note that gynecomastia is usually benign and not cancerous. A doctor can help to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and recommend the best course of treatment.
Gynecomastia Risk Factors
Risk factors for gynecomastia include being overweight or obese, using certain medications, and having a family history of the condition. Older men with a history of prostate or testicular cancer may also be at a higher risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis of gynecomastia usually entails a physical exam and a study of the patient's medical background. To rule out any underlying problems, further tests such as mammography or ultrasound may occasionally be ordered.
Treatment options for gynecomastia include medication, such as hormone therapy, and surgery. However, surgery is the most common and effective treatment option. The procedure involves the removal of excess fat and glandular tissue through liposuction or excision. In some cases, a combination of both techniques may be used.
Male breast reduction surgery or gynecomastia surgery removes excess fat and glandular tissue from the breast area in men. The surgery can take 1 to 2 hours to complete and is usually performed under general anesthesia.
During this procedure, an incision is made on the breast, and liposuction is used to remove excess fat. In some cases, excess glandular tissue may also be removed. The incision is typically made around the areola so that any resulting scar will be well-concealed. It is generally an outpatient procedure, and recovery time can vary. However, patients can usually return to work within a week or two.
There are a few different surgical techniques that can be used to perform male breast reduction surgery, depending on the specific case and the patient's desired outcome.
1. Liposuction
Liposuction is the most common method used to remove excess fat from the breast area. The procedure involves inserting a cannula (thin tube) through a small incision near the armpit or around the areola to suck out the extra fat.
2. Excision
Sometimes, liposuction alone may not be enough to achieve the desired results. In such cases, the surgeon may need to use a technique called excision, in which excess glandular tissue is removed through an incision made around the areola.
3. Combination of both techniques
In some cases, both liposuction and excision may be used to achieve the best results.
It is important to note that while male breast reduction surgery can significantly improve the appearance of the chest, the results are not permanent. Weight gain or hormonal changes can cause the breast tissue to enlarge again.
Side Effects and Recovery
Side effects of gynecomastia surgery can include pain, swelling, and bruising. There may also be a temporary loss of sensation in the chest area. In rare cases, complications can include infection, bleeding, and an uneven appearance of the chest.
Recovery time after gynecomastia surgery differs depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure.
The patient has to wear a compression garment for several weeks to help with swelling and aid healing post-surgery. For a few weeks following surgery, strenuous exercise should be avoided.
It may take several months for the chest to fully heal and for the final results to be visible.
The Bottom Line
Gynecomastia, or overdeveloped or oversized breasts in men, can be reduced through surgery. Several reasons contribute to it, including hormone abnormalities, certain drugs, and genetics. A physical examination and a study of the patient's medical history can be used to identify the illness. The most popular and efficient form of treatment is surgery, which might have minimal adverse effects. If you are a male, considering breast reduction, it is important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon who can help you understand the risks and benefits of the procedure.
To search for the best Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery healthcare providers in Croatia, Germany, Greece, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Slovakia, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, the UAE, the UK and the USA, please use the Mya Care search engine.
To search for the best doctors and healthcare providers worldwide, please use the Mya Care search engine.

Dr. Rosmy Barrios is an aesthetic medicine specialist with international work experience. She earned her physician diploma at the Universidad Del Norte’s School of Medicine in Barranquilla, Colombia, and her specialty at John F. Kennedy University in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Dr. Barrios is a member of the Pan-American Aesthetic Medicine Association (PASAM) and the Union Internationale de Médecine Esthétique (UIME). She is an expert health writer with keen interests in aesthetic medicine, regenerative aesthetics, anti-aging, fitness, and nutrition. Currently, Dr. Barrios heads the Regenerative Aesthetics department at a renowned Internal Medicine clinic based in Belgrade, Serbia.
References:
Featured Blogs



