Here Is Why You Need to Build Strong Quads

Function of the Quadriceps Femoris
Benefits of Quadriceps Muscle Strength
Importance of Quad Strength
The quadriceps muscles are the group of muscles in our anterior thigh that support various activities such as standing, walking, climbing, and running.
The quadriceps are at particular risk for strains in activities involving explosive movements. Also, the risk of injury is high in actions involving strong eccentric contractions to slow down knee flexion or hip extension.
Anatomy
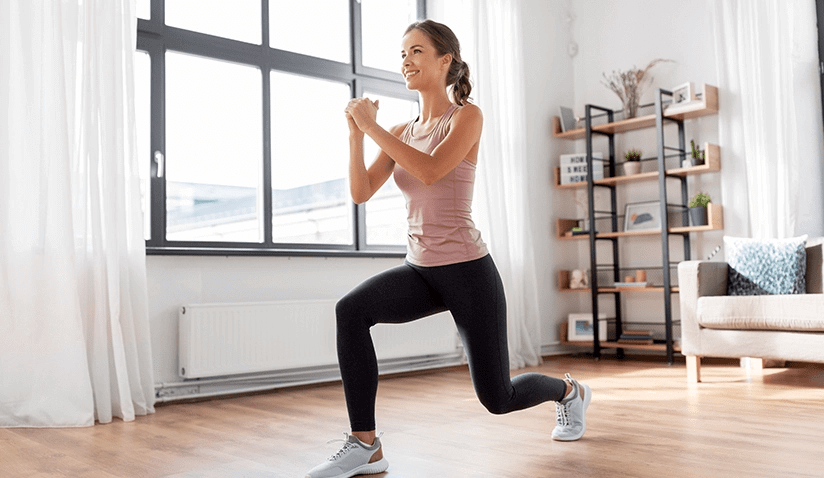
The quadriceps femoris forms the anterior muscles of the thigh along with the sartorius muscle. The term "quadriceps" means “four-headed”. As the name suggests, the quadriceps is composed of four muscles that run downward to form a common tendon attaching to the patella.
The four muscles that form the quadriceps are: rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. The tensor of the vastus intermedius, a new muscle recently added to the quadriceps femoris, gives the quadriceps a total of five muscle bellies. It is thought that the muscle corrects patellar movement and/or tenses the vastus intermedius muscle, but the exact function of the muscle is unknown.
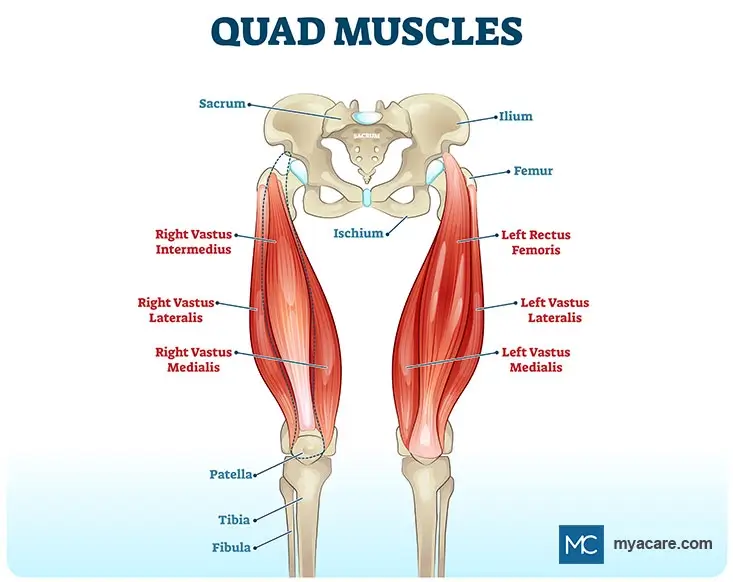
Let’s learn the anatomy of each muscle group forming the quadriceps:
Rectus femoris: This muscle arises from the hip bone, runs down the front of the thigh, covering three vastus muscles, and is attached to the patella, forming a common tendon of the quadriceps.
Vastus Lateralis: The muscle starts from the femur bone in your upper thigh and runs down to form the outer portion of the thigh before joining the kneecap. It is the largest muscle group forming the quadriceps femoris.
Vastus medialis: The muscle runs along the inner portion of the thigh, originating from the neck of the femur and inserting at the knee cap. Thus, this tear-shaped muscle connects the femur and the patella.
Vastus intermedius: The muscle lies deeper to the rectus femoris between vastus laleralis and medialis. The muscle originates from the body of the femur and inserts at the knee cap. Some parts of the muscle also form the articular muscles of the knee that insert into the knee cap.
The Function of the Quadriceps Femoris
All four muscles of the quadriceps femoris support the knee and hip joints for standing, walking, running, climbing stairs, and lifting from a chair.
The primary action of all four muscles is the extension of the lower leg at the knee joint. The Rectus femoris is also responsible for flexing the hip. The muscle group also stabilizes the knee cap, maintaining the standing position.
The sensory input from the muscle group also helps maintain and correct posture. Studies have shown that the sensory information from the quadriceps muscle group of one thigh allows its counterpart on the other side to correct posture and balance.
The Benefits of Quadriceps Muscle Strength
- Lower leg extension from the knee joint
- Flexing the hip
- Maintaining posture and balance
- Knee cap stability
- Helps in activities such as standing, walking, climbing, and running
Can Weak Quads Cause Knee Injuries?
Studies have suggested that the strength of the quadriceps muscle is associated with knee osteoarthritis, and weak quadriceps increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
Quadriceps muscle weakness is also a risk factor for non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injuries, and patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Preserve Knee Joint OA
The quadriceps muscle absorbs loads and provides dynamic stability. So, its weakness can impact weight loading, which affects the knee joint cartilage. This increases knee pain and can result in knee osteoarthritis.
In a study of resistance training in women, heavier women who did no strength training had significantly higher loading rates during gait than those who did strength training. This is due to the improved strength of the quadriceps after training.
How Can Rehabilitation Help?
Research studies have demonstrated strong evidence that physiotherapy management based on exercise effectively reduces knee pain and improves function. The major benefit of training and strengthening your quads is that it makes everyday activities such as standing, running, walking, and climbing stairs easier. Training quads will also improve kneecap stability and protect you from injuries related to the knee joint.
Exercises for Quadriceps Strength
Here are some exercises that can be done to improve Quadriceps strength:
1. Lunges

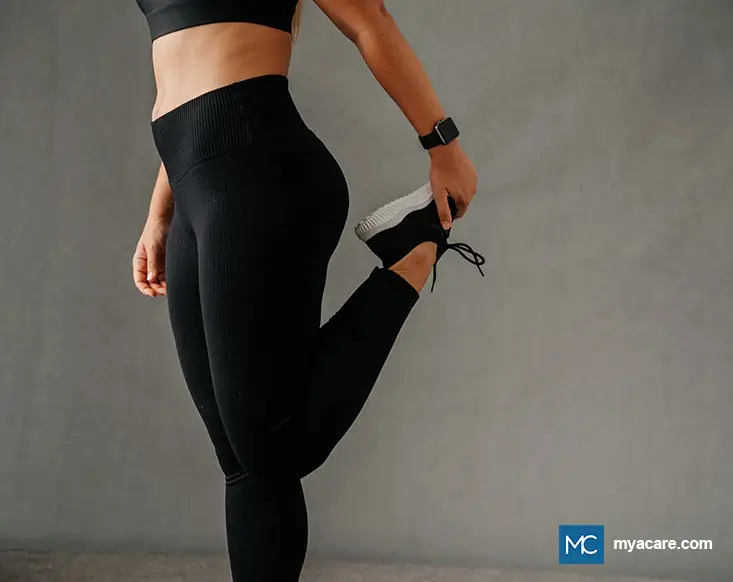
2. Quadriceps Stretches


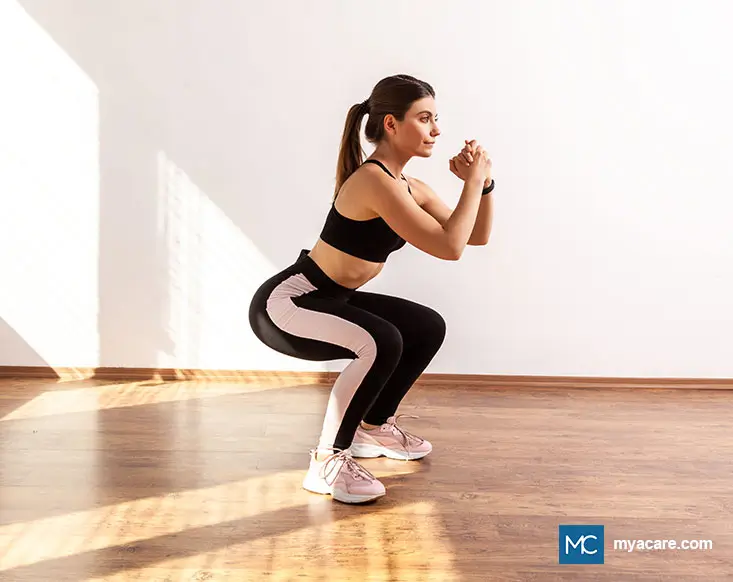
3. Squats


Jennifer Makin graduated from Salford University, Manchester, and has over 11 years of experience working across a broad range of private practices carrying out assessments on musculoskeletal injuries. She has worked extensively in semi-professional football providing pre/post-event massage, rehab plans, and pitch-side management.
References
Featured Blogs



