Xanthelasma and Non-Surgical Treatment Using Plasma Plexr Pro

Are these treatments successful?
Innovation in the treatment of XP using Plasma Plexr Pro.
Are there any recurrences with Plexr Pro?
What kind of post-procedure care is required?
Xanthelasma ("XP"), a common skin lesion (appears as yellow deposits in and around the eyes), is often ignored by patients thinking it cannot be removed or treated. Usually benign, XPs may create significant cosmetic and functional issues for the patients. This blog provides more details about XPs and an innovative treatment using plasma technology.
What is Xanthelasma?
 |
| Souce: GMV Library |
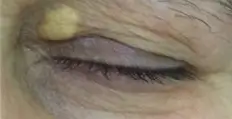
Xanthelasma, the stubborn yellow deposits, are localised cholesterol deposits beneath the eyelid skin and periorbital area. Approximately 50% of patients with XP have underlying Hyperlipidemia (a condition where one has a high level of lipids (fats, cholesterol, and triglycerides) circulating in the blood).
While these lesions are not harmful or cancerous, they can cause significant cosmetic blemishes. Patients often visit dermatologists/ cosmetic surgeons for removal and correction.
What are the Treatment Options Available?
There is no Foolproof treatment for XPs. Surgery, Cryotherapy, Electrodesiccation, Dermabrasion, Trichloroacetic acid (TCA), Lasers, and Radiofrequency (RF) have been tried and described in the literature. Some home remedies like garlic, castor oil, and apple cider vinegar have also been advocated.
Are These Treatments Successful?
Those above surgical and non-surgical treatment modalities have their respective risks and limitations. There may be a need for multiple sessions; treatment can be expensive, the depth penetration may be insufficient or too deep, causing secondary pigmentation, lid deformities, and scarring. And most importantly, there is a 30% risk of recurrence. XP is a complex deposit and needs the removal of multiple layers. It is essential to destroy all the XP cells to avoid recurrence, which can be challenging with the current treatment options. If the lesions are too deep, typical procedures can damage collateral tissue.
The ideal treatment for XP should be safe, comfortable, affordable, and provide total tissue clearance without recurrences.
Innovation in the Treatment of XP Using Plasma Plexr Pro.
Plexr Pro is the latest innovation that uses plasma to sublimate tissues. This machine is manufactured by GMV (Italy).
Plasma, a term derived from the Greek language for ‘entity’ or ‘form’, is the fourth state of matter. It consists of negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions with a net neutral charge.
 |
| Souce: GMV Library |
Plexr Pro generates plasma like a bolt of micro lightning that acts directly only on the outer layer of the skin. Before sublimating, the skin cells transmit a selective estimated quantity of energy in the form of heat, to the dermis's proper deepness, without irradiation (laser/light) or electric shock (electrosurgical unit /current). No form of energy is delivered directly from the device to the deeper tissue; no eddy currents are generated.
It is a non-invasive, non-ablative, outpatient department technique, where the air between the tip of Plexr Pro and the skin produces plasma from atmospheric gas. This focused microbeam sublimates the targeted tissue without damaging the surrounding areas. The tissue destruction is precise and controlled.
 |
| Souce: GMV Library |
What Are the Advantages of This Technique?
The advantages of this technique include excellent efficacy, minimal downtime, increased safety and predictability of results. Plexr Pro is a portable device, easy to use and ideal for office use. The cost of the treatment is affordable, the risk of damage to the eye is minimal. The other advantages of this energy are immediate contraction of the collagen fibres, collagen reorganisation, formation of new collagen, and renewal of the epidermal tissue. Hence, there is no scar or residual contraction at the site of lesion removal.
How Is it Done?
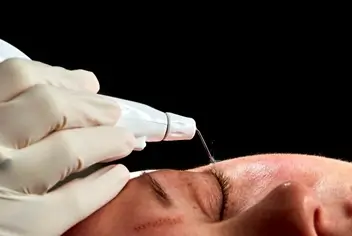
It is an outpatient procedure done under topical anaesthesia. Usually, 1 to 3 sittings are required, especially for larger XPs where multiple layers may need to be removed. The procedure time is no more than 15 to 20 min for both eyes. The spray technique is used to sublimate the layers of XP deposit, and carbonised skin particles are cleaned up.
 |
| Souce: GMV Library |
What Kind of Post-Procedure Care is Required?
The procedure may cause minor oedema and redness, persisting for a week or so. Patients are advised not to use water near the site for 24 hours, clean the face with medicated cleansers, and use Vitamin K and a sunscreen loaded with Zinc oxide. It is also recommended to avoid exposure to the sun.
What Can a Patient Expect from the Procedure?
There may be scab formation in the localised areas of the XP deposit, which usually falls off and the new epidermis scaffolds over, without any scar formation.
Are There Any Recurrences with Plexr Pro?
Plexr Pro is a reasonably new treatment modality for XPs. However, a study by Rubins et al. in 2019, amongst 15 patients with XP, indicates that there was a 100% clearance of lesions with just a single treatment. All the wounds were re-epithelialised within 1 to 2 weeks of treatment. There were no reports or evidence of scarring, dyspigmentation, or recurrence up to 12 months post-procedure. The patients expressed complete satisfaction with the cosmetic outcomes of their treatments, with no reports of pain or discomfort during or after the procedure.
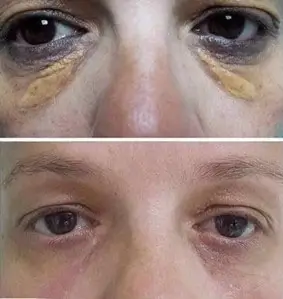
In conclusion, Xanthelasma is a complex condition, and while various treatment options are available, Plasma Plexr Pro is a cheaper, more reliable, non-invasive, and more predictable alternative to consider.
Featured Blogs



