Effect of Carbonated Drinks on Dental Health

Carbonated drinks such as soft drinks (soda pop), sparkling water, carbonated wines, and energy drinks are prepared by incorporating carbon dioxide (as dry ice or liquid) into the liquids. The addition of carbon dioxide into the water or watery liquid creates a chemical (carbonic acid) that makes the drink fizzy. It also imparts an acidic flavor and sweet sensation to your mouth.
Soft drinks contain carbonated water, sweeteners (e.g., high fructose corn syrup, sucrose, fruit juice concentrates, etc.), and flavoring agents. A 600ml bottle of soft drink contains about 10 - 16 teaspoons of sugar. The high concentration of sugars and acids in soda is associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart diseases. They are also known to damage teeth and cause tooth decay. According to a survey in 2018, the per capita soft drink consumption in the US was reported to be 38.87 gallons, second only to Mexico.
In this article, we discuss the effect of carbonated drinks on dental health.
What are the adverse effects of carbonated drinks on dental health?
Here are some of the adverse effects of carbonated drinks on dental health:
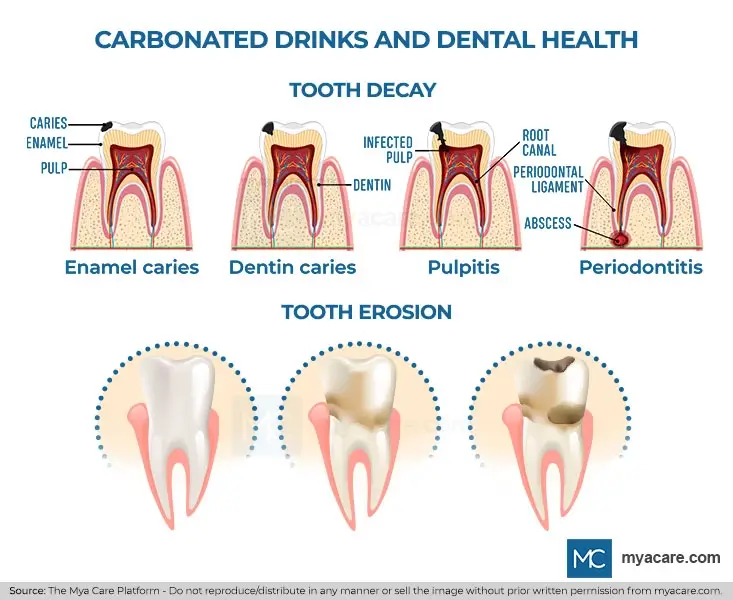
- Tooth erosion: All soft drinks or carbonated drinks have an acidic pH in the range of 1.8 to 3.5. This inherent acidity is due to the presence of acids (e.g., carbonic acids, phosphoric acid, and citric acids) which are added to enhance the taste of drinks. This pH is usually lower than the pH of the tooth enamel. The higher acidic content in the drinks tends to dissolve the outer surface of enamel causing tooth erosion. This can lead to sensitivity or pain in the tooth.
- Tooth decay: This can result from a prolonged intake of carbonated drinks and a decrease in oral hygiene practices. The sugar content in carbonated drinks or soft drinks interacts with the bacteria in the mouth to form an acid. This acid in addition to the acids present in the drinks, dissolves the outer enamel and weakens the tooth surface, causing tooth decay. Young children are at higher risk of developing tooth decay and erosions. Enamel in pre-adolescent children is porous and immature which gets demineralized by acids. The period after the eruption of primary and permanent teeth is crucial until the enamel surface matures.
How to manage the adverse effects of carbonated drinks on teeth?
Here are some of the commonly-recommended treatment options:
- Mild sensitivity can be managed with a desensitizing paste. In case of hypersensitivity, dentists may treat the eroded areas with tooth-colored resin fillings.
- In severe cases, root canal treatment followed by crown may be advised by the dentist.
What are the alternatives to soft drinks?
To reduce the risk of tooth decay and other health-related hazards, low-calorie, and sugar-free drinks, also known as diet soft drinks have become popular. These drinks are prepared using artificial sweeteners which reduce the calorie content of the drinks. However, these drinks have high acidic content which increases the risk of tooth erosion. In addition to this, due to the lack of caloric content in diet cokes, the body’s satiety reflex fails to get induced. This causes individuals to eat or drink more. Research suggests that the high intake of artificial sweeteners is a threat to the general health of an individual.
What are the recommendations for the safe consumption of soft drinks to maintain dental health?
Here are some of the recommendations to reduce the risk of damage to the teeth:
- Reduce the consumption of soft drinks: Regular intake of soft drinks damages dental and general health. So, reduce its intake in a day. For instance, if you drink daily then restrict the intake to 2-3 times a week. Once you achieve this, try to reduce it further. Individuals can also try to replace it with healthier alternatives (e.g., homemade smoothies, orange juice, green tea).
- Use a straw while having soft drinks: The use of a straw while sipping soft drinks, delivers the drink to the back of the mouth and allows only minimal contact with the teeth. Even the faster intake of the soft drink lowers the contact of sugars and acids in the soft drinks with the teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with water after the intake of soft drinks: Immediate rinsing of the mouth with plain water washes away the sugar and acidic content of soft drinks. This lessens the risk of damage to the teeth.
- Try to have food with soft drinks: Increased saliva production during chewing of food easily flushes away the acidic and sugar content of soft drinks. Individuals can also neutralize the acidic effect of soft drinks by taking cheese or milk-based beverages.
- Avoid brushing of teeth immediately: Usually, the enamel layer on the tooth softens after the intake of soft drinks. This is due to the acidic nature of the drink. Immediate brushing of such teeth causes further damage to the teeth. Hence, brushing should be performed at least 30-60 minutes after the intake of soft drinks.
- Avoid soft drinks before sleep: During sleep, the self-cleansing action of saliva is reduced. So, the acidic and sugary content of the soft drinks retain in the mouth for a long time, increasing the risk of damage to the tooth surface.
- Maintain oral hygiene: Practice brushing and flossing of teeth twice daily. Use fluoridated toothpaste while brushing. This strengthens the tooth structure and lowers the incidence of decay. In addition, visit a dentist regularly for routine checkups and professional cleaning of teeth. The dentist may also recommend fluoridated toothpaste if required.
To search for the best dentists in Germany, India, Malaysia, Poland, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, the UAE, the UK and the USA, please use the Mya Care search engine.
To search for the best healthcare providers worldwide, please use the Mya Care search engine.

Dr. Shilpy Bhandari is an experienced dental surgeon, with specialization in periodontics and implantology. She received her graduate and postgraduate education from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences in India. Besides her private practice, she enjoys writing on medical topics. She is also interested in evidence-based academic writing and has published several articles in international journals.
References:
Featured Blogs



