Types of Lung Cancer Surgery – Is Minimally-Invasive Surgery Better?
When is Lung Cancer Surgery Necessary
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death worldwide. Estimates show that 1 in 6 people have a lifetime risk of developing lung cancer.
Lung cancer surgery has come a long way in the last two decades. It is now a viable option for some patients with localized lung cancer. It involves removing a part of the lung (lobectomy), lymph nodes, or the whole affected lung (pneumonectomy). Surgery can often be curative when the cancer is in its early stage, however, other factors such as the type of surgery advised, the location of your cancer, your general health, and lung function are also important factors in deciding whether surgery is right for you.
There are several surgical options for lung cancer treatment. The traditional thoracotomy, which is the most invasive, is the most commonly performed surgery for lung cancer.
However, newer, less invasive techniques are now available in top lung cancer centers worldwide - recent minimally invasive advances in lung cancer treatment include video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and robotic surgery. In addition to finding the right treatment modality for you, it is also equally important to identify the right specialist and healthcare provider. Studies reveal that outcomes for lung cancer surgery are better at centers that operate a high volume of these procedures.
When Is Surgery Necessary For Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer surgery is not an option for all lung cancer patients.
Patients with localized (non-metastasized) lung cancer are better candidates for surgery. If lung cancer has spread to local lymph nodes, surgery might still be attempted. However, if you have metastatic lung cancer, surgery is not likely an option. Nevertheless, with the right expertise and depending on factors such as the nature of the primary tumor and the location of the metastases, procedures that show promise include:
- Video-assisted minimally invasive resection (keyhole surgery)
- Laser and / or microwave ablation (in cooperation with Radiology)
- Extensive bilateral resections
Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and carcinoid lung tumors are generally considered better candidates for surgery.
If the lung tumor is causing unbearable symptoms, palliative surgery might be attempted to provide relief, regardless of the type of tumor or spread.
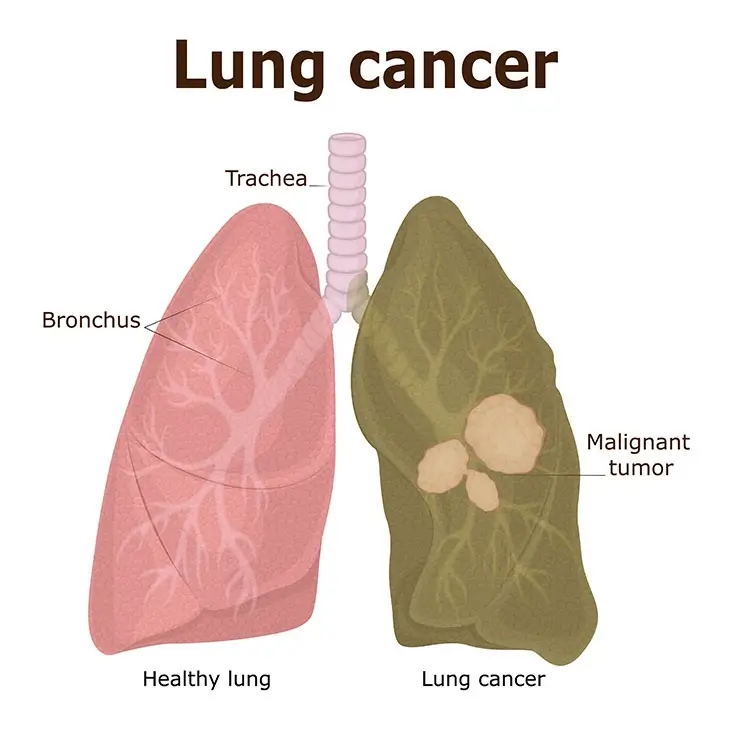
Types Of Lung Cancer Surgery
There are several types of surgeries to remove lung cancer. Thoracotomy, the traditional lung cancer surgery, is the most invasive.
Newer techniques, like VATS and robot-assisted lung cancer surgery, are now becoming a more popular option in large lung cancer centers.
The choice of procedure depends on the characteristics of the tumor, its location, and the surgeon’s expertise.
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is the traditional open surgery for lung cancer. It involves a large skin incision along the side of your chest. Your surgeon will split the chest muscles (intercostal and pectoral muscles) and enter the thoracic cavity in between the ribs.
The lung carcinoma and any surrounded lymph nodes are then cut out, and the rest of the lung is sewn shut.
After thoracotomy, you will have a large scar along the side of your chest, sometimes extending slightly to the back.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is an excellent minimally invasive surgery for lung cancer.
It’s been gaining a lot of popularity in the last couple of decades. It is a less invasive surgery for lung carcinoma.
Compared to traditional lung cancer surgery (thoracotomy), VATS is done through 4 tiny incisions, rather than a big thoracotomy incision. Your thoracic surgeon will insert a camera through one hole, and surgical instruments through the other 2 holes.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery allows your surgeon to better visualize the tumor and remove it with minimal damage to the surrounding tissue and chest wall. Post surgical pain is minimal and patients can leave the clinic early.
This leads to better results, less risks, less downtime, and quicker recovery.
Robotic Surgery
Robotic lung cancer surgery, also called robot-assisted surgery, is an advanced minimally invasive technique to treat lung cancer.
The procedure is performed with the help of a surgical robot controlled by your surgeon on a comprehensive console. The latest advances enable 3D HD video transmission and utilizes special instruments that allow greater freedom of movement than the human wrist.
Robot-assisted lung cancer surgery is partly similar to VATS. It’s done through 2-4 small incisions in the chest wall. A 3-dimensional camera is first inserted into one of the holes. Surgical instruments are inserted through the other holes to cut out the diseased lung parts.
The difference between VATS and robot lung cancer surgery is that, with the latter, the camera and instruments are held by the surgical robot. In VATS, the camera and instruments are held by the surgeon.
Your surgeon will control all the movements of the robot and camera on his control station.
What Is Involved In Lung Cancer Surgery?
Regardless of the type of lung cancer surgery you get, your surgeon will perform one or more of the following to take the diseased tissue out:
- Lobectomy: each lung is formed of several lobes. Lobectomy is the removal of a single lobe.
- Segmentectomy: each lobe is made of several segments. Segmentectomy is the removal of one or more segments, but not a full lobe.
- Wedge resection: this is the removal of a (somewhat) triangular piece of the lung, which should include the tumor.
- Pneumonectomy: this is the complete removal of the diseased lung when less invasive techniques are not possible.
Benefits Of Minimally Invasive Lung Cancer Surgery
The greatest advantage of minimally invasive lung cancer surgery is that it’s much less invasive compared to the traditional thoracotomy.
The major benefits of minimally invasive surgery for lung cancer include:
- Faster recovery and less downtime
- Cosmetic benefit - 4 tiny scars instead of a large scar along your chest
- Less pain after surgery, since less muscle trauma is involved
- Less risk of blood loss during surgery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Less trauma and tissue damage - minimal rib bone and muscle cutting
- Less risk of post-op complications
- More precise maneuvers (with robot assistance) and better visualization of the tumor with the 3D camera
These advantages make minimally invasive techniques a preferred choice for lung cancer treatment when it’s an option.
The only disadvantage of minimally invasive lung surgery is that it is technically more challenging and hence needs more time to perform. This means more time under anesthesia and more risk of anesthesia complications.
Minimally Invasive vs Traditional Surgery - Which Is Better?
When both minimally invasive and traditional surgery are viable options, then VATS and robotic surgery have a clear advantage. Previously, a deterrent for minimally invasive approaches was that they do not allow surgeons to thoroughly evaluate lymph nodes thus negatively affecting cure rate. However, recent studies reveal a substantial long-term survival benefit in patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery for early stage NSCLC. With recent advances enabling CT screening to diagnose smaller, early-stage tumors, the ability to remove them safely using MIS techniques has also improved.
The reduced trauma, easier recovery, and cosmetic benefits make minimal invasive lung cancer surgery the better choice when indicated.
Of course, there are many factors that determine whether or not you are a candidate for minimally invasive lung surgery. Your cancer care team will discuss this on a case-by-case basis to determine the best surgical option for each patient.
Risks and Complications of Lung Cancer Surgery
Lung cancer surgery is major surgery. Since it involves operating on and near vital organs, there are several risks involved:
- Pneumothorax - air leakage from the lungs
- Hemothorax - bleeding into the chest
- Heart rhythm problems
- Blood clot formation
In general, minimally invasive lung cancer surgery carries fewer surgical risks. It is important to choose a specialized center with experienced surgeons to make sure you get the best out of your lung cancer surgery.

Prof. Dr. med. Peter Kleine is the Hospital Director and Head of the Department of Thoracic Surgery at Sana Hospital Offenbach, Germany. He is also a Specialist Physician in surgery and cardiovascular surgery. Prof. Kleine has over 36 years of experience in thoracic surgery.
Sources:
Featured Blogs



