What Is a Gummy Smile and How Can It Be Fixed?
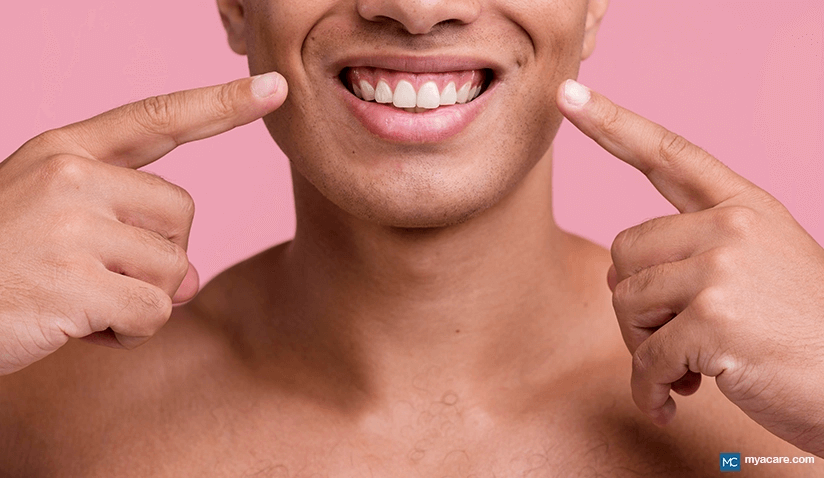

A smile with more than the desired display of gum is known as a gummy smile. It affects 10-20% of the population and is more common among women. Affected individuals may find this visually unattractive and are often self-conscious of their smile. To address this, they may seek dental treatment.
Various disorders, such as a short or hyperactive upper lip, enlargement of gums, excess growth of the upper jaw, or over eruption of front teeth, can lead to a gummy smile. The identification of the exact cause and proper diagnosis helps manage the condition appropriately.
In this article, we discuss the causes and the treatment involved in correcting a gummy smile.
How much display of gums is considered unaesthetic?
Displaying 1-2 mm of the gum on the upper jaw while smiling is considered normal and cosmetically appealing. If more than 3-4 mm of the gum is exposed while smiling, it can be perceived as unaesthetic and unpleasant. This excess display of gum is mainly evident during a smile. However, in some severe cases, it can be seen even when the lips are at rest.
What are the causes of a gummy smile?
Here are some of the reasons that may result in a gummy smile:
- Short upper lip length: The average length of the lip in young adults is around 20-24mm. Lips measuring less than 20 mm are considered short. Short lips may cause gum exposure while smiling or laughing, resulting in a gummy smile.
- Hypermobile upper lip: A hypermobile or hyperactive lip is caused by the hyperactivity of the muscle (levator labii superioris muscle), which contributes to the movement of the mouth and upper lip. This increases the exposure of the teeth and gums, causing a gummy smile.
- Altered passive eruption: After the complete eruption of a tooth in the oral cavity, gum margins shift towards the junction of the crown and root surface. If the gum margin fails to shift away from the tooth surface and overlies the major part of the tooth surface, it leads to a condition known as altered passive eruption. This results in the short appearance of the crown and an excess display of gums. In severe conditions, this may give the feeling of a hidden tooth.
- Overgrowth of gums: Gum overgrowth around the teeth can result in the excess display of gums. Here are some conditions that can result in the overgrowth of gums:
- Poor oral hygiene (Accumulation of tartar can result in inflammation and swelling of gums)
- Presence of systemic conditions (e.g., Hereditary gingival fibromatosis, leukemia)
- Regular intake of medications that are used to treat high blood pressure, seizures, or the immune system (e.g., amlodipine, phenytoin, cyclosporine)
- Excess growth of the upper jaw: If the upper jaw bone grows longer than normal, excess display of gums becomes evident. This condition is also known as Vertical Maxillary Excess (VME).
- Over- eruption of teeth: If the teeth in the front grow too far or are over-erupted, then the gums also tend to grow along with the teeth. This results in an excess display of gums. This over-eruption of teeth is also known as dentoalveolar extrusion.
In some severe cases, the gummy smile may result from a combination of multiple factors. For instance, the presence of a short lip and excess growth of the upper jaw may cause a gummy smile. Such cases require a combination of interventions to correct the smile.
How to manage a gummy smile?
Dental professionals can help diagnose the exact cause of the gummy smile using the patient’s medical history, facial and lip analysis, and oral and radiographic examination. Following this, the best treatment option will be discussed with the patient.
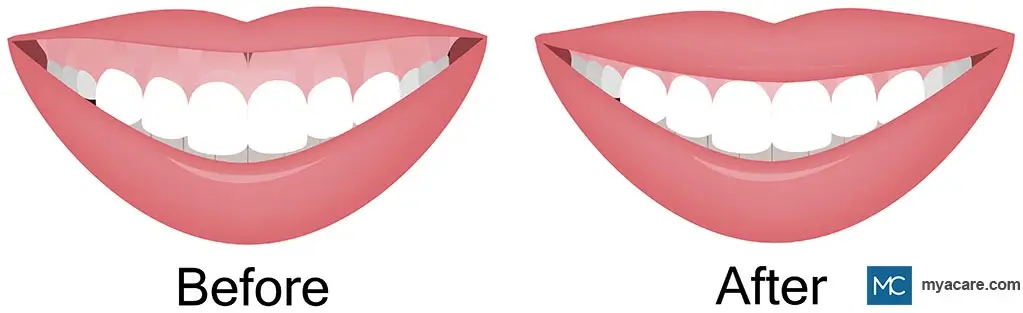
Here are some of the common treatment options available to manage a gummy smile:
a. Non-surgical treatment:
- Botox injection: Gummy smile due to the presence of a hyperactive upper lip can be treated by injecting botulinum toxin injection, also known as Botox injection. The cost of injection may vary between USD 200-300. Individuals may have to repeat the injections every 3-4 months.
- Hyaluronic acid injection: Excessive gingival display can be corrected by injecting hyaluronic injections into the hyperactive muscles (Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi), which control lip movement. Hyaluronic injections inhibit the ability of muscles to move, decreasing the upward movement of the upper lip while smiling. This injection may be required every 6-12 months, and the cost may vary between USD 500-700.
b. Surgical treatment:
- Gingivectomy: Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure to remove excess gums. This procedure results in exposing more tooth surfaces and shifting the gumline to a higher level. It is mostly used to correct gummy smiles in patients with passive altered eruptions. Gingivectomy can be performed as a standalone procedure or in combination with the reshaping of the bone underlying the gums (crown lengthening). This depends on the patient’s aesthetic expectations and how much excess gum tissue is present. The procedure may cost around USD 1,000-4,000
- Lip repositioning surgery: Lip repositioning surgery involves the removal of soft tissue from the underside of the upper lip. This restricts the muscles controlling lip movement from lifting the upper lip too high. Lip repositioning surgery masks the gummy smile by changing the position of the lips relative to the teeth. It is recommended in patients with hyperactive or short lips and mild cases of VME. This surgery may cost between USD 500 - USD 5,000, depending on the severity.
- Orthognathic surgery or orthodontic movement: Severe cases of gummy smiles due to vertical maxillary excess or dentoalveolar extrusion can be treated with orthognathic surgery. This involves repositioning the upper jaw bone with the help of surgery. The surgery is performed in combination with orthodontic treatment (straightening of teeth using braces or other appliances). In some cases, only orthodontic treatment is sufficient to improve the gummy smile. This surgery may cost around USD 20,000 - USD 40,000, and the patient may require 6-12 weeks to heal completely.
Compared to surgical options, non-surgical options are less expensive. However, non-surgical treatment options may not be applicable for all cases of excessive gum display. Consulting with your dentist will help you decide the best treatment option.
To search for the best dentists in Germany, India, Malaysia, Poland, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, the UAE, the UK and the USA, please use the Mya Care search engine.
To search for the best healthcare providers worldwide, please use the Mya Care search engine.

Dr. Shilpy Bhandari is an experienced dental surgeon, with specialization in periodontics and implantology. She received her graduate and postgraduate education from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences in India. Besides her private practice, she enjoys writing on medical topics. She is also interested in evidence-based academic writing and has published several articles in international journals.
References:
Featured Blogs



