What Is Neuroplasticity?

Updated 29 April 2024
Neuroplasticity is the propensity for nerves to modify activity as a response to some type of stimulus. The nervous system has the capacity to create new pathways. This includes the ability of the brain to rewire itself. Interaction with the environment alters the brain. While neuroplasticity is greatest at the earliest stages of development, even adults have some capacity for changes in neural connections.
How Neuroplasticity Takes Place
Neuroplasticity can occur in two ways, as discussed below.
- Reorganization of function: Parts of the brain can reorganize and take over functions previously completed by other parts. This usually happens when there is an injury in the brain.
- Regeneration of nerves: This includes synaptic plasticity where connections between the nerves can be altered. There are also nerve stem cells found in certain areas of the brain that can develop into mature neurons. Neural connections can increase through environmental factors.
Types of Neuroplasticity
Scientists have classified neuroplasticity into five types, briefly described below.
- Developmental neuroplasticity: This is the brain development during the early stages of human development from infancy to about age 3. A baby forms new connections due to exposure to different sensory experiences.
- Compensatory Masquerade: The type of neuroplasticity where the brain compensates after a traumatic brain injury or stroke.
- Homologous area adaptation: This is when a part of the brain is injured and the corresponding region in the opposite hemisphere of the brain takes over the function.
- Map expansion: As a result of learning and repetition, the brain area involved in a specific process, expands.
- Cross-modal reassignment: A type of compensation by a person who has lost a sense. For instance, a blind person can form a representation of the shape of objects by touch rather than sight.
Neuroplasticity Examples
Neuroplasticity helps people learn new things throughout their lifespan. Some of the clearest examples of neuroplasticity are the ability of functions to return in some patients who have brain injuries.
Stroke Patients and Those With Traumatic Brain Injuries
Damage to certain motor regions of the brain has been shown to bring about a change even within a hemisphere, with neural networks altering to compensate for the injury. It is important to understand that not every stroke patient or patient with neural damage can recover. Sometimes such brain injuries are lethal. However, some patients with brain injury are able to recover through rehabilitation exercises. This is a classic example of the functional reorganization of the brain.
Epilepsy and Hemispherectomy
Another clear example of neuroplasticity is seen in the hemispherectomy of young children who suffer from intractable seizures that cannot be managed any other way. In young children with severe epilepsy, the removal of the misfiring cerebral hemisphere results in a remodeling of the remaining brain tissue. The child is able to compensate for the loss of half of the brain. This is also cited as an example of homologous area adaptation. This only works in young children whose brains are still developing.
Neuroplasticity Exercises
The concept of neuroplasticity applies to everybody. Often people develop mental health issues such as depression or anxiety. Even without a specific mental health diagnosis, certain exercises can help keep the brain healthy and help a person live a fuller life. Many activities help with learning and memory. Neuroplasticity exercises can help rewire the brain and help the brain of aging individuals. Some neuroplasticity exercises are discussed below.
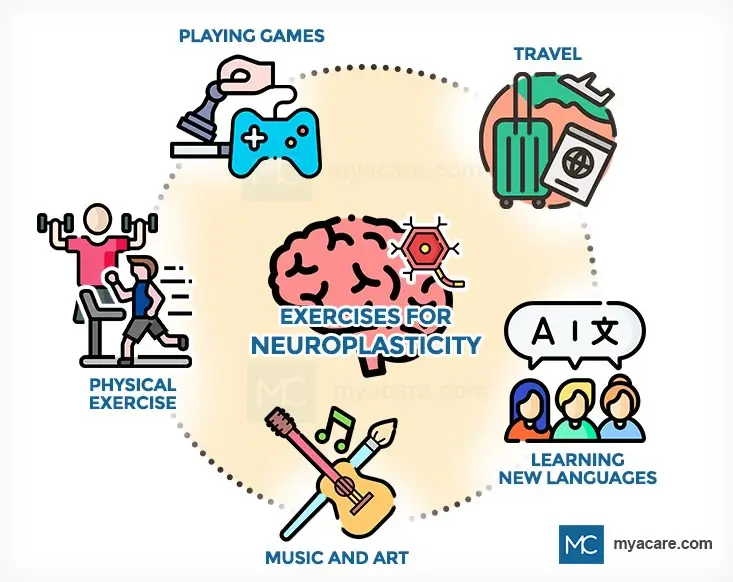
Physical Exercise
Physical activity is important in keeping your body healthy. Most people understand that exercise helps with maintaining the correct body weight and helping keep muscles and bones strong. However, physical exercise also helps your nervous system. Aerobic exercise helps increase oxygen flow to the brain as your heart beats faster. This has many benefits including better thinking, decreased stress, and improved sleep. Physical activity also reduces the risk of brain degenerative diseases such as dementia.
Travel
New experiences are good for the brain. This is why traveling is so important and valuable. Not everybody can afford to fly around the world, but even exploring new parts of the city you live in can have benefits. You can even combine exercise with travel by going for a walk in a nature reserve.
Learning a New Language
Learning another language has many benefits for the brain and even increases brain matter. It is easier when you are a child, but there is no reason you cannot learn a new language as an adult although it may take longer to accomplish. The fact is that neuroplasticity occurs when learning a new language.
Music and Art
Musicians, in general, have different brains to the rest of the population, with structures like the corpus callosum, being larger. Music affects the brain and causes neuroplasticity but the effects are strongest when we are younger. This is why it is best for children to begin learning an instrument at a young age, specifically before 7 years of age. Learning an instrument as an adult is still helpful though. This is because neuroplasticity can still happen in adults and at the very least, it can help people relax. Drawing, painting, and various other forms of creating artwork can also lead to neuroplasticity, helping your brain to form new connections.
Playing Games
Playing different types of games aids the brain in different ways. Some examples of the types of games and the benefits of each when it comes to neuroplasticity, are explained below.
- Video and computer games: These can actually help your brain. It is not healthy to play games for hours on end, but occasional gameplay is beneficial for the nervous system. Playing video games increases fine motor skills and assists in the development of spatial and visual recognition skills. In older adults, computer and video games help improve reaction times and mood.
- Puzzles: Doing puzzles increase neuroplasticity. It helps with visual and spatial intelligence and problem-solving ability. It also can help fine motor control (e.g., doing jigsaw puzzles).
Conclusion
It may appear that neuroplasticity is only relevant to infants and those who have suffered some type of brain injury. However, many of the exercises that improve neuroplasticity are beneficial for all of us in helping keep our nervous system in good condition. There are many advantages to neuroplasticity including helping with mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
To search for the best Orthopedics Healthcare Providers in Croatia, Germany, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, the UAE, UK and the USA, please use the Mya Care search engine.
To search for the best doctors and healthcare providers worldwide, please use the Mya Care search engine.

Dr. Rae Osborn has a Ph.D. in Biology from the University of Texas at Arlington. She was a tenured Associate Professor of Biology at Northwestern State University, where she taught many courses to Pre-nursing and Pre-medical students. She has written extensively on medical conditions and healthy lifestyle topics, including nutrition. She is from South Africa but lived and taught in the United States for 18 years.
Sources:
Featured Blogs



